Screening of Environmental Chemicals to Characterize Exposures in Participants With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 38129991
- PMCID: PMC11136608
- DOI: 10.1002/art.42779
Screening of Environmental Chemicals to Characterize Exposures in Participants With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: There is a need to characterize exposures associated with the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In this pilot study, we explore a hypothesis-free approach that can measure thousands of exogenous chemicals in blood ("exposome") in patients with SLE and unaffected controls.
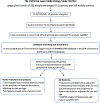
Methods: This cross-sectional study analyzed a cohort of patients with prevalent SLE (n = 285) and controls (n = 106). Plasma was analyzed by liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF/MS). Mass spectrometry features present in at least 25% of all samples were selected for association analysis (n = 2,737). Features were matched to potential chemicals using available databases. Association analysis of abundances of features with SLE status was performed, adjusting for age and sex. We also explored features associated with SLE phenotypes, sociodemographic factors, and current medication use.
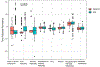
Results: We found 30 features significantly associated with SLE status (Bonferroni P < 0.05). Of these, seven matched chemical names based on databases. These seven features included phthalate metabolites, a formetanate metabolite, and eugenol. The abundance of acid pesticides differed between patients with SLE and controls (Bonferroni P < 0.05). Two unmatched features were associated with a history of lupus nephritis, and one with anti-double-stranded DNA antibody production (Bonferroni P < 0.05). Seventeen features varied by self-reported race and ethnicity, including a polyfluoroalkyl substance (analysis of variance P < 1.69 × 10-5). Eleven features correlated with antimalarials, 6 with mycophenolate mofetil, and 29 with prednisone use.
Conclusion: This proof-of-concept study demonstrates that LC-QTOF/MS is a powerful tool that agnostically detects circulating exogenous compounds. These analyses can generate hypotheses of disease-related exposures for future prospective, longitudinal studies.
© 2023 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Rheumatology. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Intramural Research Program of the National Human Genome Research Institute, NIH
- P30 AR070155/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP005120/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- K24 AR074534/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AI163359/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Lupus Research Alliance
- U01 DP006701/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- K99 ES032892/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- Scientist Development Award/Rheumatology Research Foundation
- U01DP005120/CC/CDC HHS/United States
- P30-AR-070155/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 ES032892/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

