Epidemiological, Clinical, and Laboratory Findings of 235 Hospitalized COVID-19 Adult Patients (Survivors and Non-Survivors) at Sohar Hospital in Oman
- PMID: 38130539
- PMCID: PMC10733782
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.49157
Epidemiological, Clinical, and Laboratory Findings of 235 Hospitalized COVID-19 Adult Patients (Survivors and Non-Survivors) at Sohar Hospital in Oman
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to describe the epidemiological and clinical characteristics and laboratory findings of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients at the Sohar Hospital, Sohar, Oman.
Methods: This retrospective study of admitted COVID-19 patients at Sohar Hospital in Oman was carried out from March to October 2020. Demographics and laboratory data of 19 tests for 235 COVID-19 patients, of which 202 were survivors and 33 were non-survivors, were collected from the hospital information system after ethics approval.
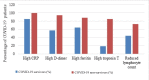
Results: Thirteen factors were significantly correlated with in-hospital mortality, including older age, having chronic disease, high neutrophil count, high troponin T, high creatinine, low albumin (p < 0.0001), high white blood cell (WBC) count, low hemoglobin, high D-dimer (p < 0.001), high C-reactive protein (CRP) (p < 0.002), low lymphocyte count (p < 0.003), high alkaline phosphatase (ALP) enzyme (p < 0.007) and high ferritin (p < 0.045). The most common laboratory blood test abnormalities that were highly correlated with mortality were increased values of CRP (100% of non-survivors), D-dimer (94.1% of non-survivors), ferritin (88.2% of non-survivors), and troponin T (85% of non-survivors) and reduced lymphocyte count (73.9% of non-survivors).
Conclusion: These findings could help in categorizing COVID-19 patients for risk-based assessment and early identification of patients with poor prognosis.
Keywords: coronavirus; covid-19; d-dimer; elevated c-reactive protein (crp); epidemiology; high ferritin; high troponin t; laboratory investigation; prognosis; survival.
Copyright © 2023, Al Khan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low Vitamin D Status at Admission as a Risk Factor for Poor Survival in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: An Italian Retrospective Study.J Am Nutr Assoc. 2022 Mar-Apr;41(3):250-265. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2021.1877580. Epub 2021 Feb 18. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2022. PMID: 33600292 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Profile and Determinants of Mortality in Patients With COVID-19: A Retrospective Analytical Cross-Sectional Study in a Tertiary Care Center in South India.Cureus. 2022 Mar 12;14(3):e23103. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23103. eCollection 2022 Mar. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35464560 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of Demographic and Clinical Characteristics on Disease Severity and Mortality in Patients with Confirmed COVID-19.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Jun 29;14:2989-3000. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S317350. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34234528 Free PMC article.
-
Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Jun 25;58(7):1021-1028. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0369. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32286245 Review.
-
Correlations of Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jul 13;17(14):5026. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17145026. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32668763 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Patient Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes During the 2020-2021 COVID-19 Wave: An Observational Study at a Tertiary Hospital in Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2024 Oct 9;16(10):e71119. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71119. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39386928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The COVID-19 Innovation Timeline. [ Mar; 2023 ]. 2022. https://covidtimeline.ifpma.org/ https://covidtimeline.ifpma.org/
-
- Worldometer: Oman. [ Sep; 2023 ]. 2020. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/oman/ https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/oman/
-
- Worldometer: COVID-19. [ Oct; 2021 ]. 2021. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous