A study on the recognition of monkeypox infection based on deep convolutional neural networks
- PMID: 38130718
- PMCID: PMC10733491
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1225557
A study on the recognition of monkeypox infection based on deep convolutional neural networks
Abstract
Introduction: The World Health Organization (WHO) has assessed the global public risk of monkeypox as moderate, and 71 WHO member countries have reported more than 14,000 cases of monkeypox infection. At present, the identification of clinical symptoms of monkeypox mainly depends on traditional medical means, which has the problems of low detection efficiency and high detection cost. The deep learning algorithm is excellent in image recognition and can extract and recognize image features quickly and reliably.
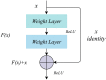
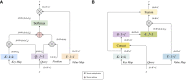
Methods: Therefore, this paper proposes a residual convolutional neural network based on the λ function and contextual transformer (LaCTResNet) for the image recognition of monkeypox cases.
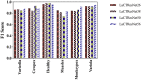
Results: The average recognition accuracy of the neural network model is 91.85%, which is 15.82% higher than that of the baseline model ResNet50 and better than the classical convolutional neural networks models such as AlexNet, VGG16, Inception-V3, and EfficientNet-B5.
Discussion: This method realizes high-precision identification of skin symptoms of the monkeypox virus to provide a fast and reliable auxiliary diagnosis method for monkeypox cases for front-line medical staff.
Keywords: aided diagnosis; contextual transformer; deep learning; monkeypox images; residual convolutional networks.
Copyright © 2023 Chen and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
MpoxNet: dual-branch deep residual squeeze and excitation monkeypox classification network with attention mechanism.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jun 7;14:1397316. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1397316. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38912211 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging convolutional neural networks and hashing techniques for the secure classification of monkeypox disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 4;14(1):26579. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75030-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39496621 Free PMC article.
-
White blood cells detection and classification based on regional convolutional neural networks.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Feb;135:109472. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109472. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 31760248
-
Automated Monkeypox Skin Lesion Detection Using Deep Learning and Transfer Learning Techniques.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Mar 1;20(5):4422. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20054422. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36901430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the power of convolutional neural networks in melanoma diagnosis.Eur J Dermatol. 2023 Oct 1;33(5):495-505. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2023.4559. Eur J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 38297925
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence in assisting pathogenic microorganism diagnosis and treatment: a review of infectious skin diseases.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 8;15:1467113. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1467113. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39439939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang M, Cui F. Status of epidemiology and prevention and control of monkeypox. Jiangsu J Prev Med (2023) 34(01):8–11. doi: 10.13668/j.issn.1006-9070.2023.01.002 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

