The impact of Sars-Cov-2 infection on the wound healing of cervical treatment in patients with squamous intraepithelial lesions: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38131047
- PMCID: PMC10733498
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1222767
The impact of Sars-Cov-2 infection on the wound healing of cervical treatment in patients with squamous intraepithelial lesions: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: SARS-CoV-2 infection has been associated with an increase in inflammatory factors, a weakening of the immune system, and a potentially delay in wound healing following surgery or ablative treatment. In this retrospective cohort study, we aimed to investigate the impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on wound healing following cervical treatment in patients with squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL).
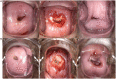
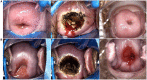
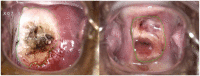
Method: From November 2022 to February 2023, patients with SIL who underwent cervical ablative treatment or loop electrosurgical excision procedure at the People's Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China, were enrolled in the study. Of these, 29 patients who developed symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection and confirmed by an antigen test within one month after cervical treatment were included as experimental group, while the other 31 patients who received cervical treatment after recovering from SARS-CoV-2 infection were included in the control group. The cervical wound condition of all patients was documented using colposcopy immediately and one month after the procedure. Image J software was utilized to analyze the wound healing rate at one month post-treatment, and the wound healing status between two groups was compared. A vaginal discharge examination was performed before and one month after cervical treatment.
Results: No significant differences in age, severity, treatment, or time between groups. Experimental group had significantly lower healing rate 83.77(62.04, 97.09) % than control 98.64(97.10, 99.46)%,p < 0.001, and a higher scab non-shedding rate (24.14% vs. 3.22%, p = 0.024). Among patients who were infected with SARS-CoV-2 after undergoing cervical treatment, we observed 5 out of 7 patients (71.43%) contracted SARS-CoV-2 within 2 weeks after cervical treatment. No significant correlation was found between white blood cell count or leukocyte esterase in vaginal discharge and delayed wound healing of the cervix (p = 0.947 and 0.970, respectively).
Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 infection may prolong the healing time of cervical treatment in patients with SIL. To minimize the risk of delayed healing, it's crucial for patients to avoid viral infections such as SARS-CoV-2 within the first month of treatment. Taking necessary precautions to prevent infection is essential for successful cervical treatment outcomes in patients with SIL.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; ablative treatment; cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion; loop electrosurgical excision procedure; wound healing.
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Wu, Li, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of local photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid for the treatment of cervical low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions with high-risk HPV infection: A retrospective study.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021 Mar;33:102172. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.102172. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021. PMID: 33401023
-
[Clinical analysis of cervical intraepithelial lesion in postmenopausal women].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Oct 25;53(10):705-710. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2018.10.010. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30369128 Chinese.
-
Small lesion size measured by colposcopy may predict absence of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in a large loop excision of the transformation zone specimen.BJOG. 2017 Feb;124(3):495-502. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.14247. Epub 2016 Aug 9. BJOG. 2017. PMID: 27506510
-
Histopathological discrepancies between colposcopy-directed biopsy and LEEP-conization observed during SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.Ginekol Pol. 2023;94(1):12-18. doi: 10.5603/GP.a2022.0081. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Ginekol Pol. 2023. PMID: 36043301
-
[Discussion on the diagnosis and treatment of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions in post-menopausal women].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jun 25;54(6):393-398. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2019.06.007. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31262123 Chinese.
References
-
- Grigore M, Cruickshank ME, Nieminen P, Tjalma W, Moss E, Redman C. National guidelines for management of cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion: a survey of european federation for colposcopy members. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (2021) 256:46–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.10.028 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

