Recent Advances in Nanowire-Based Wearable Physical Sensors
- PMID: 38131785
- PMCID: PMC10742341
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13121025
Recent Advances in Nanowire-Based Wearable Physical Sensors
Abstract
Wearable electronics is a technology that closely integrates electronic devices with the human body or clothing, which can realize human-computer interaction, health monitoring, smart medical, and other functions. Wearable physical sensors are an important part of wearable electronics. They can sense various physical signals from the human body or the surrounding environment and convert them into electrical signals for processing and analysis. Nanowires (NW) have unique properties such as a high surface-to-volume ratio, high flexibility, high carrier mobility, a tunable bandgap, a large piezoresistive coefficient, and a strong light-matter interaction. They are one of the ideal candidates for the fabrication of wearable physical sensors with high sensitivity, fast response, and low power consumption. In this review, we summarize recent advances in various types of NW-based wearable physical sensors, specifically including mechanical, photoelectric, temperature, and multifunctional sensors. The discussion revolves around the structural design, sensing mechanisms, manufacture, and practical applications of these sensors, highlighting the positive role that NWs play in the sensing process. Finally, we present the conclusions with perspectives on current challenges and future opportunities in this field.
Keywords: health monitoring; human–machine interfaces; nanowires; wearable electronics; wearable sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




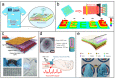

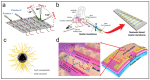
References
-
- Yin R., Wang D., Zhao S., Lou Z., Shen G. Wearable Sensors-Enabled Human–Machine Interaction Systems: From Design to Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2008936. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202008936. - DOI
-
- Wang K., Yap L.W., Gong S., Wang R., Wang S., Cheng W. Nanowire-Based Soft Wearable Human–Machine Interfaces for Future Virtual and Augmented Reality Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2008347. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202008347. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

