Design and User Experience of VirNE Application: Deep Breathing Exercise in a Virtual Natural Environment to Reduce Treatment Anxiety in Pediatrics
- PMID: 38132019
- PMCID: PMC10743239
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11243129
Design and User Experience of VirNE Application: Deep Breathing Exercise in a Virtual Natural Environment to Reduce Treatment Anxiety in Pediatrics
Abstract
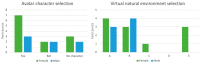
Treatment anxiety is a serious problem among child patients. A few studies have addressed this issue with virtual reality solutions, with promising results; however, the applications used have generally been designed for entertainment instead of this purpose. This article studies the potential of using deep breathing exercises in a virtual natural environment to address this issue, with a focus on design approach and user experience. It presents the VirNE-Virtual Natural Environments relaxation application, which is based on known stress-reduction methods, and a feasibility study conducted with it in a local hospital. The study had a within-subjects design, and it included 21 eight to twelve-year-old child patients, who used the application during an intravenous cannulation procedure related to their treatment. The study found good user acceptance and user experience both among the child patients and pediatricians, with the perceived usefulness of the method being higher among the patients with increased levels of anxiety or needle phobia. In addition, a clear stress-reducing effect was found. This offers proof-of-concept for the multidisciplinary design approach based on existing scientific knowledge regarding the desired effect for pediatric virtual reality applications for this use context.
Keywords: analgesia; anxiety; child; deep breathing; nature; stress; user experience; virtual natural environments; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Case Report: Virtual natural environment solution helped a child cope with a painful procedure.Front Pediatr. 2024 May 2;12:1355046. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1355046. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38756972 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Using Guided Deep Breathing Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment to Reduce Stress during Pediatric Treatment.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;11(24):3140. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11243140. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132030 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Personalization in the User Experience, Preferences and Engagement with Virtual Reality Environments for Relaxation.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 13;19(12):7237. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127237. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35742483 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Reality for Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Comprehensive Review.JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2023 Oct 2;10:e47114. doi: 10.2196/47114. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2023. PMID: 37782529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychological therapy using virtual reality for treatment of driving phobia: a systematic review.Disabil Rehabil. 2023 May;45(10):1582-1594. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2022.2069293. Epub 2022 May 9. Disabil Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 35532316
Cited by
-
Case Report: Virtual natural environment solution helped a child cope with a painful procedure.Front Pediatr. 2024 May 2;12:1355046. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1355046. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38756972 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Using Guided Deep Breathing Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment to Reduce Stress during Pediatric Treatment.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;11(24):3140. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11243140. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pate J.T., Blount R.L., Cohen L.L., Smith A.J. Childhood Medical Experience and Temperament as Predictors of Adult Functioning in Medical Situations. Child. Health Care. 1996;25:281–298. doi: 10.1207/s15326888chc2504_4. - DOI
-
- Xiang H., Shen J., Wheeler K.K., Patterson J., Lever K., Armstrong M., Shi J., Thakkar R.K., Groner J.I., Noffsinger D., et al. Efficacy of Smartphone Active and Passive Virtual Reality Distraction vs. Standard Care on Burn Pain Among Pediatric Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open. 2021;4:e2112082. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.12082. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferraz-Torres M., San Martín-Rodríguez L., García-Vivar C., Soto-Ruiz N., Escalada-Hernández P. Passive or Interactive Virtual Reality? The Effectiveness for Pain and Anxiety Reduction in Pediatric Patients. Virtual Real. 2022;26:1307–1316. doi: 10.1007/s10055-022-00633-7. - DOI
-
- Simonetti V., Tomietto M., Comparcini D., Vankova N., Marcelli S., Cicolini G. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality in the Management of Paediatric Anxiety during the Peri-operative Period: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2022;125:104115. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2021.104115. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

