Patients' Expectations and Satisfaction with the Patient-Doctor Relationship in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- PMID: 38132029
- PMCID: PMC10742400
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11243139
Patients' Expectations and Satisfaction with the Patient-Doctor Relationship in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Abstract
Introduction: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory dermatosis with a vast psychosocial burden. We analyzed the actual and ideal patient-doctor relationship and patients' satisfaction with the patient-doctor relationship in relation to their satisfaction with life (SWL), HS-related quality of life, and psychopathological symptoms.
Methods: 105 HS patients (53% females; mean age 37.64 ± 14.01 years) were enrolled. Severity of the disease was measured using Hurley staging and the International HS Score System (IHS4). Instruments utilized: Patient Expectation Test; Satisfaction with Life Scale; HS Quality of Life; Patient Health Questionnaire-9; Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7; General Health Questionnaire.
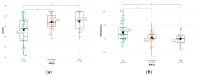
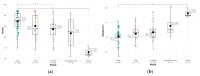
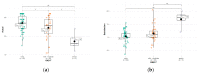
Results: Patients with Hurley I and mild IHS4 had the lowest satisfaction with the patient-doctor relationship. There were significant correlations between the actual patient-doctor relationship and the patients' SWL (r = 0.30; p = 0.002), depressive (r = -0.36; p < 0.01), anxiety (r = 0.37; p < 0.01) and psychopathological symptoms (r = -0.47; p < 0.0001) and between the satisfaction with the patient-doctor relationship and their SWL (r = -0.32; p = 0.00098). Multiple regression analysis revealed a significant influence of the following factors: Hurley II + III, psychopathological symptoms, and severe anxiety about the actual patient-doctor relationship and the satisfaction with the patient-doctor relationship.
Conclusions: Assessment of relations between patients and doctors is related to the patients' mental health and SWL. The usage of the Patient Expectation Test in clinical practice can improve the patient-doctor relationship and the general quality of care for and compliance by HS patients.
Keywords: acne inversa; hidradenitis suppurativa; patient–doctor relationship; psychopathological symptoms; satisfaction with life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Satisfaction with Life and Coping Strategies among Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 7;12(8):2755. doi: 10.3390/jcm12082755. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37109092 Free PMC article.
-
Two Cases of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treated with Adalimumab at the Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Clinical Hospital Mostar.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021 Jul;29(2):108-110. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021. PMID: 34477078
-
Self-Reported Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity: Is It Useful for Clinical Practice?Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022 Apr;12(4):899-909. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00701-5. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35274220 Free PMC article.
-
Overview and comparison of the clinical scores in hidradenitis suppurativa: A real-life clinical data.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 17;10:1145152. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1145152. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37138732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence-based approach to the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa, based on the European guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016 Sep;17(3):343-351. doi: 10.1007/s11154-016-9328-5. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 26831295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Profound Sexual Dysfunction Among Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Cross-sectional Study.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024 Jul;14(7):1823-1838. doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01196-y. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38869824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fabrazzo M., Cipolla S., Signoriello S., Camerlengo A., Calabrese G., Giordano G.M., Argenziano G., Galderisi S. A Systematic Review on Shared Biological Mechanisms of Depression and Anxiety in Comorbidity with Psoriasis, Atopic Dermatitis, and Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Eur. Psychiatry. 2021;64:e71. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.2249. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

