Rare Pancreatic/Peripancreatic Cystic Lesions Can Be Accurately Characterized by EUS with Through-the-Needle Biopsy-A Unique Pictorial Essay with Clinical and Histopathological Correlations
- PMID: 38132247
- PMCID: PMC10743172
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13243663
Rare Pancreatic/Peripancreatic Cystic Lesions Can Be Accurately Characterized by EUS with Through-the-Needle Biopsy-A Unique Pictorial Essay with Clinical and Histopathological Correlations
Abstract
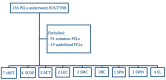
Due to their aspecific macroscopic appearance, uncommon pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) are often misdiagnosed as mucinous lesions and improperly resected. We aimed to evaluate the endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided through-the-needle biopsy (TTNB) capacity of the preoperative diagnosis of uncommon PCLs. Overall, 136 patients with PCLs who underwent EUS-TTNB between 2016 and 2022 were retrospectively identified. Common histotypes (e.g., IPMN, serous cystadenoma, and mucinous cystadenoma) were excluded and 26 (19.1%) patients (15 female, mean age 52.9 ± 10.4) were analyzed. The EUS findings, adverse events (AEs), and TTNB outcomes in uncommon PCLs were evaluated. The cysts histotype was accurately diagnosed by TTNB in 24/26 (92.3%) cases (seven cystic neuroendocrine tumors, four squamoid cysts, three acinar cells cystadenomas, two lymphoepithelial cysts, two mucinous non-neoplastic cysts, two bronchogenic cysts, two cystic lymphangiomas, one solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm, and one schwannoma). In the remaining two cases, lymphangioma was eventually diagnosed after resection. Surgery was performed in 15/26 (57.7%) patients. The mean follow-up of non-surgical patients was 32.5 months. One severe acute case of pancreatitis (3.8%) that required surgery occurred after EUS-TTNB. Uncommon pancreatic/peripancreatic lesions represent the 19.1% of PCLs in our series, with mainly benign histotypes. TTNB demonstrated a high diagnostic performance with a low rate of AEs in this setting, representing a reliable tool with which to avoid useless surgery.
Keywords: endoscopic ultrasound; fine-needle aspiration; pancreatic cancer; pancreatic cyst; pancreatic surgery; through-the-needle biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Mizuno S., Nakai Y., Yoshikawa T., Ishigaki K., Matsubara S., Yamamoto N., Ijichi H., Tateishi K., Tada M., Hayashi N., et al. Prevalence of pancreatic cystic lesions is associated with diabetes mellitus and obesity: An analysis of 5296 individuals who underwent a preventive medical examination. Pancreas. 2017;46:801–805. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka M., Fernández-Del Castillo C., Kamisawa T., Jang J.Y., Levy P., Ohtsuka T., Salvia R., Shimizu Y., Tada M., Wolfgang C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2017;17:738–753. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.07.007. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

