Octopus vulgaris Exhibits Interindividual Differences in Behavioural and Problem-Solving Performance
- PMID: 38132313
- PMCID: PMC10740590
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12121487
Octopus vulgaris Exhibits Interindividual Differences in Behavioural and Problem-Solving Performance
Abstract
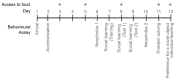
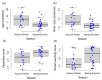
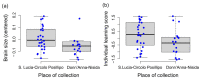
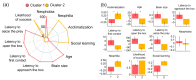
By presenting individual Octopus vulgaris with an extractive foraging problem with a puzzle box, we examined the possible correlation between behavioural performances (e.g., ease of adaptation to captive conditions, prevalence of neophobic and neophilic behaviours, and propensity to learn individually or by observing conspecifics), biotic (body and brain size, age, sex) and abiotic (seasonality and place of origin) factors. We found more neophilic animals showing shorter latencies to approach the puzzle box and higher probability of solving the task; also, shorter times to solve the task were correlated with better performance on the individual learning task. However, the most neophilic octopuses that approached the puzzle box more quickly did not reach the solution earlier than other individuals, suggesting that strong neophilic tendency may lead to suboptimal performance at some stages of the problem-solving process. In addition, seasonal and environmental characteristics of location of origin appear to influence the rate of expression of individual traits central to problem solving. Overall, our analysis provides new insights into the traits associated with problem solving in invertebrates and highlights the presence of adaptive mechanisms that promote population-level changes in octopuses' behavioural traits.
Keywords: behavioural plasticity; cephalopods; extractive foraging; innovation; neophilia; octopus; problem solving; seasonality; social learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Personality and problem-solving in common mynas (Acridotheres tristis).Behav Processes. 2017 Jan;134:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2016.09.013. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Behav Processes. 2017. PMID: 27717852 Review.
-
The role of stimulus preexposure in problem solving by Octopus vulgaris.Anim Cogn. 1998 Oct;1(2):107-12. doi: 10.1007/s100710050015. Anim Cogn. 1998. PMID: 18953584
-
A standardized battery of tests to measure Octopus vulgaris' behavioural performance.Invert Neurosci. 2020 Feb 14;20(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s10158-020-0237-7. Invert Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32060722
-
Urbanization and its effects on personality traits: a result of microevolution or phenotypic plasticity?Glob Chang Biol. 2013 Sep;19(9):2634-44. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12258. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Glob Chang Biol. 2013. PMID: 23681984
-
Innovation and problem solving: a review of common mechanisms.Behav Processes. 2014 Nov;109 Pt B:121-34. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2014.08.027. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Behav Processes. 2014. PMID: 25245306 Review.
Cited by
-
Bivalve Shell Utilization by Juvenile Octopus vulgaris in Sandy Substrates.Ecol Evol. 2025 May 15;15(5):e71060. doi: 10.1002/ece3.71060. eCollection 2025 May. Ecol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40386488 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic, molecular, and cellular divergence of the human brain.Trends Neurosci. 2024 Jul;47(7):491-505. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2024.05.009. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Trends Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38897852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weiss A.S. The Epic of the Cephalopod. Discourse. 2002;24:150–159. doi: 10.1353/dis.2003.0018. - DOI
-
- Caddel J., DeVries M. Eight Arms of Inspiration: The Octopus Art Project. Memento Publishing and Out of Step Books; Los Angeles CA, USA: 2013. p. 336.
-
- Montgomery S. The Octopus Scientists: Exploring the Mind of a Mollusk. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt; Boston, MA, USA: 2015. p. 71.
-
- Montgomery S. The Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of Consciousness. Atria Books; New York, NY, USA: 2016. p. 272.
-
- Nakajima R., Shigeno S., Zullo L., De Sio F., Schmidt M.R. Cephalopods between science, art, and engineering: A contemporary synthesis. Front. Commun. 2018;3:20. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2018.00020. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

