Steroid-Induced Hyperglycemia and Its Effect on Outcomes of R-CHOP Chemotherapy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 38132372
- PMCID: PMC10742719
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol30120738
Steroid-Induced Hyperglycemia and Its Effect on Outcomes of R-CHOP Chemotherapy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
Large doses of steroids are integral to R-CHOP, a first-line systemic therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), an aggressive form of non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL). Patients on R-CHOP often develop clinically significant hyperglycemia from steroids. There is evidence of harms from steroid-induced hyperglycemia in the context of chemotherapy which are associated with a reduction in overall survival. The objective of our study was to characterize the effect of steroid-induced hyperglycemia on the outcomes of R-CHOP chemotherapy for DLBCL.
Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review of 188 patients with DLBCL treated with R-CHOP through CancerCare Manitoba (CCMB) from 1 January 2010 to 31 December 2014. Patients diagnosed with DLBCL were identified using the Manitoba Cancer Registry. The CCMB electronic medical record was reviewed to examine the association between steroid-induced hyperglycemia and subsequent infection, including febrile neutropenic events and overall survival (OS).
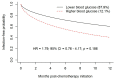
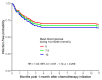
Results: Patients who developed hyperglycemia with steroid exposure became hyperglycemic during their first R-CHOP cycle. No significant differences in OS or rates of infection were found between euglycemic and hyperglycemic subjects.
Conclusions: Patients destined to develop steroid-induced hyperglycemia declare themselves early in the course of steroid exposure. No statistically significant reduction in overall survival attributable to steroid-induced hyperglycemia was found.
Keywords: hyperglycemia; lymphoma; steroid; toxicities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impact of age group on febrile neutropenia risk assessment and management in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP regimens.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2012 Oct;12(5):297-305. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2012.06.004. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2012. PMID: 23040435 Clinical Trial.
-
Combination of ibrutinib with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) for treatment-naive patients with CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a non-randomised, phase 1b study.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Aug;15(9):1019-26. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70311-0. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25042202 Clinical Trial.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
R-CHOP compared to R-CHOP + X for newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Oncol. 2021 Jun;60(6):744-749. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2021.1898048. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Acta Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33734921
-
Hyperglycemia during first-line R-CHOP or dose adjusted R-EPOCH chemotherapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma is prevalent and associated with chemotherapy alteration - a retrospective study.Leuk Lymphoma. 2018 Aug;59(8):1871-1877. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1410889. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018. PMID: 29252084 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of dynamic changes in metabolic syndrome components with clinical outcomes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 16;15:1524498. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1524498. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40589637 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous glucose monitoring to characterize hyperglycemia during chemotherapy for early stage breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Aug;212(3):511-519. doi: 10.1007/s10549-025-07745-z. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40468140
References
-
- Weiser M.A., Cabanillas M.E., Konopleva M., Thomas D.A., Pierce S.A., Escalante C.P., Kantarjian H.M., O’Brien S.M. Relation between the duration of remission and hyperglycemia during induction chemotherapy for acute lymphocytic leukemia with a hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone/methotrexate–cytarabine regimen. Cancer. 2004;100:1179–1185. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20071. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lamar Z.S., Dothard A., Kennedy L., Isom S., Robinson M., Vaidya R., Hurd D., McClain D., Lesser G. Hyperglycemia during first-line R-CHOP or dose adjusted R-EPOCH chemotherapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma is prevalent and associated with chemotherapy alteration—A retrospective study. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2018;59:1871–1877. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1410889. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

