Patient Dose Estimation in Computed Tomography-Guided Biopsy Procedures
- PMID: 38132685
- PMCID: PMC10744458
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging9120267
Patient Dose Estimation in Computed Tomography-Guided Biopsy Procedures
Abstract
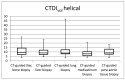
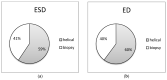
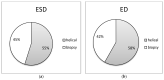
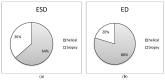
This study establishes typical Diagnostic Reference Levels (DRL) values and assesses patient doses in computed tomography (CT)-guided biopsy procedures. The Effective Dose (ED), Entrance Skin Dose (ESD), and Size-Specific Dose Estimate (SSDE) were calculated using the relevant literature-derived conversion factors. A retrospective analysis of 226 CT-guided biopsies across five categories (Iliac bone, liver, lung, mediastinum, and para-aortic lymph nodes) was conducted. Typical DRL values were computed as median distributions, following guidelines from the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) Publication 135. DRLs for helical mode CT acquisitions were set at 9.7 mGy for Iliac bone, 8.9 mGy for liver, 8.8 mGy for lung, 7.9 mGy for mediastinal mass, and 9 mGy for para-aortic lymph nodes biopsies. In contrast, DRLs for biopsy acquisitions were 7.3 mGy, 7.7 mGy, 5.6 mGy, 5.6 mGy, and 7.4 mGy, respectively. Median SSDE values varied from 7.6 mGy to 10 mGy for biopsy acquisitions and from 11.3 mGy to 12.6 mGy for helical scans. Median ED values ranged from 1.6 mSv to 5.7 mSv for biopsy scans and from 3.9 mSv to 9.3 mSv for helical scans. The study highlights the significance of using DRLs for optimizing CT-guided biopsy procedures, revealing notable variations in radiation exposure between helical scans covering entire anatomical regions and localized biopsy acquisitions.
Keywords: CT-guided biopsies; diagnostic reference levels; patient dose.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Radiation exposure, organ and effective dose of CT-guided liver biopsy as a function of lesion depth and size.J Radiol Prot. 2022 Jul 27;42(3). doi: 10.1088/1361-6498/ac7e80. J Radiol Prot. 2022. PMID: 35790148
-
Radiation exposure of image-guided intrathecal administration of nusinersen to adult patients with spinal muscular atrophy.Neuroradiology. 2019 May;61(5):565-574. doi: 10.1007/s00234-019-02189-x. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Neuroradiology. 2019. PMID: 30868184
-
Institutional clinical indication-based typical dose values of multiphasic abdominopelvic computed tomography examinations.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2024 Feb 20. doi: 10.4274/dir.2024.232551. Online ahead of print. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38375738
-
An Analysis of Computed Tomography Diagnostic Reference Levels in India Compared to Other Countries.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;14(15):1585. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14151585. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis on the radiation dose of computed tomography in hybrid nuclear medicine imaging.EJNMMI Phys. 2023 May 25;10(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40658-023-00553-8. EJNMMI Phys. 2023. PMID: 37227561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IMV Medical Information Division 2019 Global Imaging Market Outlook Report. [(accessed on 2 February 2022)]. Available online: https://imvinfo.com/product/imv-2019-global-imaging-market-outlook-report/
-
- Faiella E., Messina L., Castiello G., Bernetti C., Pacella G., Altomare C., Andresciani F., Sarli M., Longo F., Crucitti P., et al. Augmented reality 3D navigation system for percutaneous CT-guided pulmonary ground-glass opacity biopsies: A comparison with the standard CT-guided technique. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022;14:247–256. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-1285. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

