Dapagliflozin in patients with critical illness: rationale and design of the DEFENDER study
- PMID: 38133155
- PMCID: PMC10734800
- DOI: 10.5935/2965-2774.20230129-en
Dapagliflozin in patients with critical illness: rationale and design of the DEFENDER study
Abstract
Background: Critical illness is a major ongoing health care burden worldwide and is associated with high mortality rates. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors have consistently shown benefits in cardiovascular and renal outcomes. The effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in acute illness have not been properly investigated.
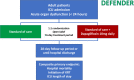
Methods: DEFENDER is an investigator-initiated, multicenter, randomized, open-label trial designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in 500 adult participants with acute organ dysfunction who are hospitalized in the intensive care unit. Eligible participants will be randomized 1:1 to receive dapagliflozin 10mg plus standard of care for up to 14 days or standard of care alone. The primary outcome is a hierarchical composite of hospital mortality, initiation of kidney replacement therapy, and intensive care unit length of stay, up to 28 days. Safety will be strictly monitored throughout the study.
Conclusion: DEFENDER is the first study designed to investigate the use of a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor in general intensive care unit patients with acute organ dysfunction. It will provide relevant information on the use of drugs of this promising class in critically ill patients.
Clinicaltrials.gov registry: NCT05558098.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Kober L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, Ponikowski P, Sabatine MS, Anand IS, Bělohlávek J, Böhm M, Chiang CE, Chopra VK, de Boer RA, Desai AS, Diez M, Drozdz J, Dukát A, Ge J, Howlett JG, Katova T, Kitakaze M, Ljungman CE, Merkely B, Nicolau JC, O’Meara E, Petrie MC, Vinh PN, Schou M, Tereshchenko S, Verma S, Held C, DeMets DL, Docherty KF, Jhund PS, Bengtsson O, Sjöstrand M, Langkilde AM, DAPA-HF Trial Committees and Investigators Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(21):1995–2008. - PubMed
-
- Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, Januzzi J, Verma S, Tsutsui H, Brueckmann M, Jamal W, Kimura K, Schnee J, Zeller C, Cotton D, Bocchi E, Böhm M, Choi DJ, Chopra V, Chuquiure E, Giannetti N, Janssens S, Zhang J, Gonzalez Juanatey JR, Kaul S, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Merkely B, Nicholls SJ, Perrone S, Pina I, Ponikowski P, Sattar N, Senni M, Seronde MF, Spinar J, Squire I, Taddei S, Wanner C, Zannad F, EMPEROR-Reduced Trial Investigators Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(15):1413–1424. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Bocchi E, Bohm M, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Choi DJ, Chopra V, Chuquiure-Valenzuela E, Giannetti N, Gomez-Mesa JE, Janssens S, Januzzi JL, Gonzalez-Juanatey JR, Merkely B, Nicholls SJ, Perrone SV, Piña IL, Ponikowski P, Senni M, Sim D, Spinar J, Squire I, Taddei S, Tsutsui H, Verma S, Vinereanu D, Zhang J, Carson P, Lam CS, Marx N, Zeller C, Sattar N, Jamal W, Schnaidt S, Schnee JM, Brueckmann M, Pocock SJ, Zannad F, Packer M, EMPEROR-Preserved Trial Investigators Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(16):1451–1461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical