The Role of α3β1 Integrin Modulation on Fabry Disease Podocyte Injury and Kidney Impairment
- PMID: 38133204
- PMCID: PMC10748128
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins15120700
The Role of α3β1 Integrin Modulation on Fabry Disease Podocyte Injury and Kidney Impairment
Abstract
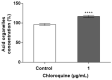
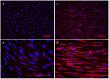
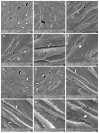
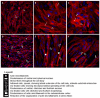
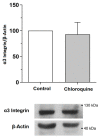
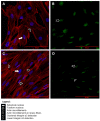
Podocyte dysfunction plays a crucial role in renal injury and is identified as a key contributor to proteinuria in Fabry disease (FD), primarily impacting glomerular filtration function (GFF). The α3β1 integrins are important for podocyte adhesion to the glomerular basement membrane, and disturbances in these integrins can lead to podocyte injury. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the effects of chloroquine (CQ) on podocytes, as this drug can be used to obtain an in vitro condition analogous to the FD. Murine podocytes were employed in our experiments. The results revealed a dose-dependent reduction in cell viability. CQ at a sub-lethal concentration (1.0 µg/mL) induced lysosomal accumulation significantly (p < 0.0001). Morphological changes were evident through scanning electron microscopy and immunofluorescence, highlighting alterations in F-actin and nucleus morphology. No significant changes were observed in the gene expression of α3β1 integrins via RT-qPCR. Protein expression of α3 integrin was evaluated with Western Blotting and immunofluorescence, demonstrating its lower detection in podocytes exposed to CQ. Our findings propose a novel in vitro model for exploring secondary Fabry nephropathy, indicating a modulation of α3β1 integrin and morphological alterations in podocytes under the influence of CQ.
Keywords: Fabry disease; chloroquine; podocyte injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bichet D.G., Aerts J.M., Auray-Blais C., Maruyama H., Mehta A.B., Skuban N., Krusinska E., Schiffmann R. Assessment of Plasma Lyso-Gb3 for Clinical Monitoring of Treatment Response in Migalastat-Treated Patients with Fabry Disease. Genet. Med. 2021;23:192–201. doi: 10.1038/s41436-020-00968-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

