Dynamin-related protein 1 is a critical regulator of mitochondrial calcium homeostasis during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 38133921
- PMCID: PMC12027350
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202301040RR
Dynamin-related protein 1 is a critical regulator of mitochondrial calcium homeostasis during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
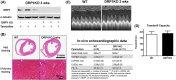
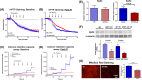
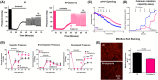
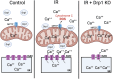
Dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) is a cytosolic GTPase protein that when activated translocates to the mitochondria, meditating mitochondrial fission and increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cardiomyocytes. Drp1 has shown promise as a therapeutic target for reducing cardiac ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury; however, the lack of specificity of some small molecule Drp1 inhibitors and the reliance on the use of Drp1 haploinsufficient hearts from older mice have left the role of Drp1 in IR in question. Here, we address these concerns using two approaches, using: (a) short-term (3 weeks), conditional, cardiomyocyte-specific, Drp1 knockout (KO) and (b) a novel, highly specific Drp1 GTPase inhibitor, Drpitor1a. Short-term Drp1 KO mice exhibited preserved exercise capacity and cardiac contractility, and their isolated cardiac mitochondria demonstrated increased mitochondrial complex 1 activity, respiratory coupling, and calcium retention capacity compared to controls. When exposed to IR injury in a Langendorff perfusion system, Drp1 KO hearts had preserved contractility, decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS), enhanced mitochondrial calcium capacity, and increased resistance to mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) opening. Pharmacological inhibition of Drp1 with Drpitor1a following ischemia, but before reperfusion, was as protective as Drp1 KO for cardiac function and mitochondrial calcium homeostasis. In contrast to the benefits of short-term Drp1 inhibition, prolonged Drp1 ablation (6 weeks) resulted in cardiomyopathy. Drp1 KO hearts were also associated with decreased ryanodine receptor 2 (RyR2) protein expression and pharmacological inhibition of the RyR2 receptor decreased ROS in post-IR hearts suggesting that changes in RyR2 may have a role in Drp1 KO mediated cardioprotection. We conclude that Drp1-mediated increases in myocardial ROS production and impairment of mitochondrial calcium handling are key mechanisms of IR injury. Short-term inhibition of Drp1 is a promising strategy to limit early myocardial IR injury which is relevant for the therapy of acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, and heart transplantation.
© 2023 The Authors. The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures



References
-
- Hannah Ritchie FSAMR. Causes of death. OurWorldInData.org; 2018.
-
- Jiaquan X, Murphy SL, Kochanek KD, Arias E. Mortality in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics; 2021.
-
- Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1121‐1135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

