Extended Postexposure Protection Against Vaginal Simian/Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection With Tenofovir Alafenamide Fumarate/Elvitegravir Inserts in Macaques
- PMID: 38134382
- PMCID: PMC11457164
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiad599
Extended Postexposure Protection Against Vaginal Simian/Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection With Tenofovir Alafenamide Fumarate/Elvitegravir Inserts in Macaques
Abstract
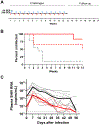
Vaginal inserts that can be used on demand before or after sex may be a desirable human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) prevention option for women. We recently showed that inserts containing tenofovir alafenamide fumarate (TAF, 20 mg) and elvitegravir (EVG, 16 mg) were highly protective against repeated simian/human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) vaginal exposures when administered to macaques 4 hours before or after virus exposure (93% and 100%, respectively). Here, we show in the same macaque model that insert application 8 hours or 24 hours after exposure maintains high efficacy (94.4% and 77.2%, respectively). These data extend the protective window by TAF/EVG inserts and inform their clinical development for on-demand prophylaxis in women.
Keywords: HIV preexposure and postexposure prophylaxis; elvitegravir; macaque models; tenofovir alafenamide; topical PrEP and PEP.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. J. G. G.-L. and W. H. are named in US government patents on “Inhibition of HIV infection through chemoprophylaxis” (US patents 9,044,509 B2; 9,579,333 B2; 9,937,191 B2 and 10,335,423 B2) and “HIV post-exposure prophylaxis” (US patent 11,191,763 B2), and the US government patent application on “HIV preexposure prophylaxis.” (US 2022/0265689 A1). M. M. P., V. A., G. F. D., and M. R. C. are named in patent applications US 2021/0379089 A1 on “Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of making on-demand solid dosage formulations,” inventions that were developed under a USAID-funded cooperative agreement. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Joint United Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). Global HIV and AIDS statistics—fact sheet. Geneva, Switzerland: UNAIDS, 2022.
-
- AVAC. PrEp work: investment in more options must continue, and faster, smarter rollout must be a top priority. https://www.avac.org/prevention-option/prep. Accessed 18 July 2023.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

