Natural Products Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 2B6 Activity and Methadone Metabolism
- PMID: 38135504
- PMCID: PMC10877711
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.123.001578
Natural Products Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 2B6 Activity and Methadone Metabolism
Abstract
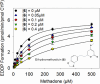
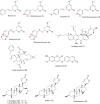
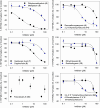
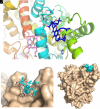
Methadone is cleared predominately by hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2B6-catalyzed metabolism to inactive metabolites. CYP2B6 also catalyzes the metabolism of several other drugs. Methadone and CYP2B6 are susceptible to pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions. Use of natural products such as herbals and other botanicals is substantial and growing, and concomitant use of prescription medicines and non-prescription herbals is common and may result in interactions, often precipitated by CYP inhibition. Little is known about herbal product effects on CYP2B6 activity, and CYP2B6-catalyzed methadone metabolism. We screened a family of natural product compounds used in traditional medicines, herbal teas, and synthetic analogs of compounds found in plants, including kavalactones, flavokavains, chalcones and gambogic acid, for inhibition of expressed CYP2B6 activity and specifically inhibition of CYP2B6-mediated methadone metabolism. An initial screen evaluated inhibition of CYP2B6-catalyzed 7-ethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl) coumarin O-deethylation. Hits were further evaluated for inhibition of racemic methadone metabolism, including mechanism of inhibition and kinetic constants. In order of decreasing potency, the most effective inhibitors of methadone metabolism were dihydromethysticin (competitive, K i 0.074 µM), gambogic acid (noncompetitive, K i 6 µM), and 2,2'-dihydroxychalcone (noncompetitive, K i 16 µM). Molecular modeling of CYP2B6-methadone and inhibitor binding showed substrate and inhibitor binding position and orientation and their interactions with CYP2B6 residues. These results show that CYP2B6 and CYP2B6-catalyzed methadone metabolism are inhibited by certain natural products, at concentrations which may be clinically relevant. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: This investigation identified several natural product constituents which inhibit in vitro human recombinant CYP2B6 and CYP2B6-catalyzed N-demethylation of the opioid methadone. The most potent inhibitors (K i) were dihydromethysticin (0.074 µM), gambogic acid (6 µM) and 2,2'-dihydroxychalcone (16 µM). Molecular modeling of ligand interactions with CYP2B6 found that dihydromethysticin and 2,2'-dihydroxychalcone bound at the active site, while gambogic acid interacted with an allosteric site on the CYP2B6 surface. Natural product constituents may inhibit CYP2B6 and methadone metabolism at clinically relevant concentrations.
Copyright © 2024 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Stereoselective metabolism of methadone N-demethylation by cytochrome P4502B6 and 2C19.Chirality. 2004 Jan;16(1):36-44. doi: 10.1002/chir.10303. Chirality. 2004. PMID: 14628297
-
Methadone N-demethylation by the common CYP2B6 allelic variant CYP2B6.6.Drug Metab Dispos. 2013 Apr;41(4):709-13. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.050625. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013. PMID: 23298862 Free PMC article.
-
Enantiomeric metabolic interactions and stereoselective human methadone metabolism.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Apr;321(1):389-99. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.117580. Epub 2007 Jan 26. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17259447
-
Multidisciplinary Insights into the Structure-Function Relationship of the CYP2B6 Active Site.Drug Metab Dispos. 2023 Mar;51(3):369-384. doi: 10.1124/dmd.122.000853. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Drug Metab Dispos. 2023. PMID: 36418184 Review.
-
Metabolomics of methadone: clinical and forensic toxicological implications and variability of dose response.Drug Metab Rev. 2016 Nov;48(4):568-576. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2016.1192642. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Drug Metab Rev. 2016. PMID: 27320437 Review.
References
-
- Angle ED, Cox PM (2023) Multidisciplinary Insights into the Structure-Function Relationship of the CYP2B6 Active Site. Drug Metab Dispos 51:369–384. - PubMed
-
- Anke J, Ramzan I (2004) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interactions with Kava (Piper methysticum Forst. f.). J Ethnopharmacol 93:153–160. - PubMed
-
- Chang TK, Crespi CL, Waxman DJ (2006) Determination of CYP2B6 component of 7-ethoxy-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin O-deethylation activity in human liver microsomes. Methods Mol Biol 320:97–102. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
