ABCA7 deficiency causes neuronal dysregulation by altering mitochondrial lipid metabolism
- PMID: 38135757
- PMCID: PMC11153016
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-023-02372-w
ABCA7 deficiency causes neuronal dysregulation by altering mitochondrial lipid metabolism
Abstract
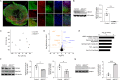
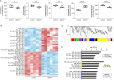
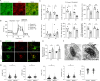
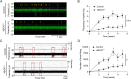
ABCA7 loss-of-function variants are associated with increased risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Using ABCA7 knockout human iPSC models generated with CRISPR/Cas9, we investigated the impacts of ABCA7 deficiency on neuronal metabolism and function. Lipidomics revealed that mitochondria-related phospholipids, such as phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin were reduced in the ABCA7-deficient iPSC-derived cortical organoids. Consistently, ABCA7 deficiency-induced alterations of mitochondrial morphology accompanied by reduced ATP synthase activity and exacerbated oxidative damage in the organoids. Furthermore, ABCA7-deficient iPSC-derived neurons showed compromised mitochondrial respiration and excess ROS generation, as well as enlarged mitochondrial morphology compared to the isogenic controls. ABCA7 deficiency also decreased spontaneous synaptic firing and network formation in iPSC-derived neurons, in which the effects were rescued by supplementation with phosphatidylglycerol or NAD+ precursor, nicotinamide mononucleotide. Importantly, effects of ABCA7 deficiency on mitochondria morphology and synapses were recapitulated in synaptosomes isolated from the brain of neuron-specific Abca7 knockout mice. Together, our results provide evidence that ABCA7 loss-of-function contributes to AD risk by modulating mitochondria lipid metabolism.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TK consults Ono Pharma, Inc. YAM is currently an employee of SciNeuro Pharmaceuticals. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RF1AG057181/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- RF1 AG068034/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013319/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG068034/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- U19AG069701/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- RF1AG081203/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- P30 AG044271/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG069701/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057181/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061729/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG071226/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG071226/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- RF1 AG081203/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG071226/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

