BlobCUT: A Contrastive Learning Method to Support Small Blob Detection in Medical Imaging
- PMID: 38135963
- PMCID: PMC10740534
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10121372
BlobCUT: A Contrastive Learning Method to Support Small Blob Detection in Medical Imaging
Abstract
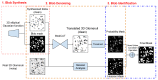
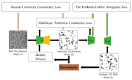
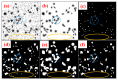
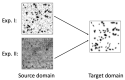
Medical imaging-based biomarkers derived from small objects (e.g., cell nuclei) play a crucial role in medical applications. However, detecting and segmenting small objects (a.k.a. blobs) remains a challenging task. In this research, we propose a novel 3D small blob detector called BlobCUT. BlobCUT is an unpaired image-to-image (I2I) translation model that falls under the Contrastive Unpaired Translation paradigm. It employs a blob synthesis module to generate synthetic 3D blobs with corresponding masks. This is incorporated into the iterative model training as the ground truth. The I2I translation process is designed with two constraints: (1) a convexity consistency constraint that relies on Hessian analysis to preserve the geometric properties and (2) an intensity distribution consistency constraint based on Kullback-Leibler divergence to preserve the intensity distribution of blobs. BlobCUT learns the inherent noise distribution from the target noisy blob images and performs image translation from the noisy domain to the clean domain, effectively functioning as a denoising process to support blob identification. To validate the performance of BlobCUT, we evaluate it on a 3D simulated dataset of blobs and a 3D MRI dataset of mouse kidneys. We conduct a comparative analysis involving six state-of-the-art methods. Our findings reveal that BlobCUT exhibits superior performance and training efficiency, utilizing only 56.6% of the training time required by the state-of-the-art BlobDetGAN. This underscores the effectiveness of BlobCUT in accurately segmenting small blobs while achieving notable gains in training efficiency.
Keywords: Hessian analysis; blob detection; contrastive learning; glomeruli segmentation; imaging biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Jennifer R. Charlton is co-owner of Sindri Technologies, LLC; consultant for XN Biotechnologies; consultant for Medtronics; President Elect of the Board of the Neonatal Kidney Collaborative; investor in Zorro-Flow. Author Kevin M. Bennett is co-owner of XN Biotechnologies, LLC, Sindri Technologies LLC, and Nephrodiagnostics, LLC. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved small blob detection in 3D images using jointly constrained deep learning and Hessian analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 15;10(1):326. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57223-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31941994 Free PMC article.
-
Small Blob Detector Using Bi-Threshold Constrained Adaptive Scales.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2021 Sep;68(9):2654-2665. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2020.3046252. Epub 2021 Aug 23. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 33347401 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Small Blob Detection Based on Local Convexity, Intensity and Shape Information.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016 Apr;35(4):1127-37. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2509463. Epub 2015 Dec 17. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26685229 Free PMC article.
-
Small blob identification in medical images using regional features from optimum scale.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015 Apr;62(4):1051-62. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2014.2360154. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015. PMID: 25265624
-
High-ISO Long-Exposure Image Denoising Based on Quantitative Blob Characterization.IEEE Trans Image Process. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2986687. Online ahead of print. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2020. PMID: 32305916
Cited by
-
Enhanced Data Mining and Visualization of Sensory-Graph-Modeled Datasets through Summarization.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 14;24(14):4554. doi: 10.3390/s24144554. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065952 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography using contrastive unpaired translation.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31366. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82839-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39733058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang S., Chen X., Duan J., Mou X. A CNN-based hybrid ring artifact reduction algorithm for CT images. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2020;5:253–260. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2020.2983391. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

