Bilosomes and Biloparticles for the Delivery of Lipophilic Drugs: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 38136145
- PMCID: PMC10741235
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12122025
Bilosomes and Biloparticles for the Delivery of Lipophilic Drugs: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
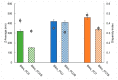
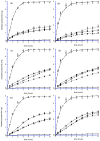
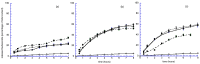
In this study, bile acid-based vesicles and nanoparticles (i.e., bilosomes and biloparticles) are studied to improve the water solubility of lipophilic drugs. Ursodeoxycholic acid, sodium cholate, sodium taurocholate and budesonide were used as bile acids and model drugs, respectively. Bilosomes and biloparticles were prepared following standard protocols with minor changes, after a preformulation study. The obtained systems showed good encapsulation efficiency and dimensional stability. Particularly, for biloparticles, the increase in encapsulation efficiency followed the order ursodeoxycholic acid < sodium cholate < sodium taurocholate. The in vitro release of budesonide from both bilosytems was performed by means of dialysis using either a nylon membrane or a portion of Wistar rat small intestine and two receiving solutions (i.e., simulated gastric and intestinal fluids). Both in gastric and intestinal fluid, budesonide was released from bilosystems more slowly than the reference solution, while biloparticles showed a significant improvement in the passage of budesonide into aqueous solution. Immunofluorescence experiments indicated that ursodeoxycholic acid bilosomes containing budesonide are effective in reducing the inflammatory response induced by glucose oxidase stimuli and counteract ox-inflammatory damage within intestinal cells.
Keywords: NLC; SLN; bile acids; drug solubility; immunofluorescence; inflammasome; nanoparticles; nanotechnology; nanovesicles; poorly water-soluble drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Facilitated permeation of insulin across TR146 cells by cholic acid derivatives-modified elastic bilosomes.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Sep 6;13:5173-5186. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S168310. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30233179 Free PMC article.
-
Anionic versus cationic bilosomes as oral nanocarriers for enhanced delivery of the hydrophilic drug risedronate.Int J Pharm. 2019 Jun 10;564:410-425. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.04.069. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31029657
-
Investigating the potential of employing bilosomes as a novel vesicular carrier for transdermal delivery of tenoxicam.Int J Pharm. 2015 May 15;485(1-2):329-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.03.033. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25796122
-
Emerging Trends in Bilosomes as Therapeutic Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 23;16(6):697. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060697. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile Salt Stabilized Vesicles (Bilosomes): A Novel Nano-Pharmaceutical Design for Oral Delivery of Proteins and Peptides.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(11):1575-1588. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170124111142. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28120725 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibiotic-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Current Challenges and Emerging Alternative Therapies.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 16;13(4):913. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040913. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Modulation of Cell Plasticity by Budesonide: Beyond the Metabolic and Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Glucocorticoids.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 11;17(4):504. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040504. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stojančević M., Pavlović N., Goločorbin-Kon S., Mikov M. Application of Bile Acids in Drug Formulation and Delivery. Front. Life Sci. 2013;7:112–122. doi: 10.1080/21553769.2013.879925. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

