Memory Recovery Effect of a New Bioactive Innovative Combination in Rats with Experimental Dementia
- PMID: 38136170
- PMCID: PMC10740861
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12122050
Memory Recovery Effect of a New Bioactive Innovative Combination in Rats with Experimental Dementia
Abstract
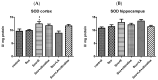
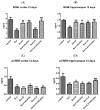
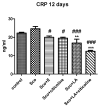
Alzheimer's disease manifests as a complex pathological condition, with neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and cholinergic dysfunction being a few of the many pathological changes. Due to the complexity of the disease, current therapeutic strategies aim at a multitargeted approach, often relying on a combination of substances with versatile and complementary effects. In the present study, a unique combination of α-lipoic acid, citicoline, extracts of leaves from olive tree and green tea, vitamin D3, selenium and an immune-supporting complex was tested in scopolamine-induced dementia in rats. Using behavioral and biochemical methods, we assessed the effects of the combination on learning and memory, and elucidated the mechanisms of these effects. Our results showed that, compared to its components, the experimental combination was most efficient in improving short- and long-term memory as assessed by the step-through method as well as spatial memory as assessed by T-maze and Barnes maze underlined by decreases in AChE activity (p < 0.05) and LPO (p < 0.001), increases in SOD activity in the cortex (p < 0.05) and increases in catalase (p < 0.05) and GPx (p < 0.01) activities and BDNF (p < 0.001) and pCREB (p < 0.05) levels in the hippocampus. No significant histopathological changes or blood parameter changes were detected, making the experimental combination an effective and safe candidate in a multitargeted treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; citicoline; extract of leaves green tea; extract of leaves olive tree; scopolamine; selenium; vitamin D3; α-lipoic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be regarded as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
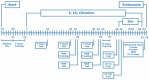
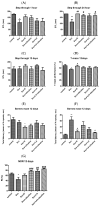
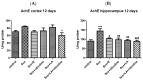
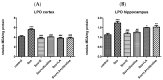



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

