Protective Role of Taurine on Rat Offspring Hypertension in the Setting of Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 38136178
- PMCID: PMC10740461
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12122059
Protective Role of Taurine on Rat Offspring Hypertension in the Setting of Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
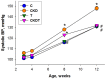
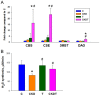
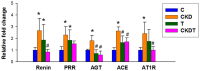
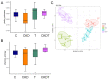
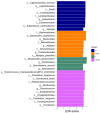
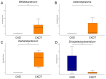
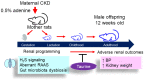
Taurine is a natural antioxidant with antihypertensive properties. Maternal chronic kidney disease (CKD) has an impact on renal programming and increases the risk of offspring hypertension in later life. The underlying mechanisms cover oxidative stress, a dysregulated hydrogen sulfide (H2S) system, dysbiotic gut microbiota, and inappropriate activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). We investigated whether perinatal taurine administration enables us to prevent high blood pressure (BP) in offspring complicated by maternal CKD. Before mating, CKD was induced through feeding chow containing 0.5% adenine for 3 weeks. Taurine was administered (3% in drinking water) during gestation and lactation. Four groups of male offspring were used (n = 8/group): controls, CKD, taurine-treated control rats, and taurine-treated rats with CKD. Taurine treatment significantly reduced BP in male offspring born to mothers with CKD. The beneficial effects of perinatal taurine treatment were attributed to an augmented H2S pathway, rebalance of aberrant RAAS activation, and gut microbiota alterations. In summary, our results not only deepen our knowledge of the mechanisms underlying maternal CKD-induced offspring hypertension but also afford us the impetus to consider taurine-based intervention as a promising preventive approach for future clinical translation.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaDs); gut microbiota; hypertension; nitric oxide; renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS); taurine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Programs Hypertension in Adult Male Rat Offspring: Implications of Nitric Oxide and Gut Microbiome Derived Metabolites.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 30;21(19):7237. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197237. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33008046 Free PMC article.
-
Protection by Means of Perinatal Oral Sodium Thiosulfate Administration against Offspring Hypertension in a Rat Model of Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 26;12(7):1344. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071344. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507884 Free PMC article.
-
Lactoferrin Supplementation during Pregnancy and Lactation Protects Adult Male Rat Offspring from Hypertension Induced by Maternal Adenine Diet.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 8;16(16):2607. doi: 10.3390/nu16162607. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203744 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System to Prevent Hypertension and Kidney Disease of Developmental Origins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2298. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052298. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids, Hydrogen Sulfide, and Sulfur Compounds on Kidney Health and Disease.Metabolites. 2023 May 25;13(6):688. doi: 10.3390/metabo13060688. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37367846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short Communication: Taurine Long-Term Treatment Prevents the Development of Cardiac Hypertrophy, and Premature Death in Hereditary Cardiomyopathy of the Hamster Is Sex-Independent.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 26;16(7):946. doi: 10.3390/nu16070946. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38612980 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Dietary Strategies for Improving Offspring Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health: A Scoping Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 10;25(18):9788. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189788. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337276 Free PMC article.
-
The Renin-Angiotensin System and Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: Focus on Early-Life Programming.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 14;25(6):3298. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063298. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal Models for Studying Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 12;13(2):452. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020452. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breastfeeding and Future Cardiovascular, Kidney, and Metabolic Health-A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 12;17(6):995. doi: 10.3390/nu17060995. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40290039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Hypertension. 2023. [(accessed on 6 October 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension.
-
- WHO . Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension in Adults. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

