The NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor, Mitoapocynin, Mitigates DFP-Induced Reactive Astrogliosis in a Rat Model of Organophosphate Neurotoxicity
- PMID: 38136181
- PMCID: PMC10740988
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12122061
The NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor, Mitoapocynin, Mitigates DFP-Induced Reactive Astrogliosis in a Rat Model of Organophosphate Neurotoxicity
Abstract
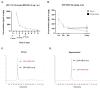
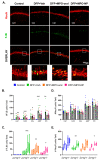
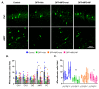
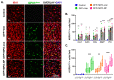
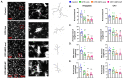
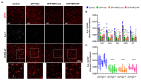
NADPH oxidase (NOX) is a primary mediator of superoxides, which promote oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and neuroinflammation after diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) intoxication. Although orally administered mitoapocynin (MPO, 10 mg/kg), a mitochondrial-targeted NOX inhibitor, reduced oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines in the periphery, its efficacy in the brain regions of DFP-exposed rats was limited. In this study, we encapsulated MPO in polyanhydride nanoparticles (NPs) based on 1,6-bis(p-carboxyphenoxy) hexane (CPH) and sebacic anhydride (SA) for enhanced drug delivery to the brain and compared with a high oral dose of MPO (30 mg/kg). NOX2 (GP91phox) regulation and microglial (IBA1) morphology were analyzed to determine the efficacy of MPO-NP vs. MPO-oral in an 8-day study in the rat DFP model. Compared to the control, DFP-exposed animals exhibited significant upregulation of NOX2 and a reduced length and number of microglial processes, indicative of reactive microglia. Neither MPO treatment attenuated the DFP effect. Neurodegeneration (FJB+NeuN) was significantly greater in DFP-exposed groups regardless of treatment. Interestingly, neuronal loss in DFP+MPO-treated animals was not significantly different from the control. MPO-oral rescued inhibitory neuronal loss in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Notably, MPO-NP and MPO-oral significantly reduced astrogliosis (absolute GFAP counts) and reactive gliosis (C3+GFAP). An analysis of inwardly rectifying potassium channels (Kir4.1) in astroglia revealed a significant reduction in the brain regions of the DFP+VEH group, but MPO had no effect. Overall, both NP-encapsulated and orally administered MPO had similar effects. Our findings demonstrate that MPO effectively mitigates DFP-induced reactive astrogliosis in several key brain regions and protects neurons in CA1, which may have long-term beneficial effects on spontaneous seizures and behavioral comorbidities. Long-term telemetry and behavioral studies and a different dosing regimen of MPO are required to understand its therapeutic potential.
Keywords: DFP (diisopropyl fluorophosphate); GP91phox; Kir4.1; NADPH oxidase (NOX); astrogliosis; nanoparticles; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Dudek F.E., Staley K.J. Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies. 4th ed. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2012. The time course and circuit mechanisms of acquired epileptogenesis. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

