Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review from the Oxidative Stress to the Management of Related Diseases
- PMID: 38136211
- PMCID: PMC10740837
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12122091
Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review from the Oxidative Stress to the Management of Related Diseases
Abstract
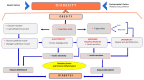
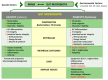
Metabolic syndrome (MS) is a growing disorder affecting thousands of people worldwide, especially in industrialised countries, increasing mortality. Oxidative stress, hyperglycaemia, insulin resistance, inflammation, dysbiosis, abdominal obesity, atherogenic dyslipidaemia and hypertension are important factors linked to MS clusters of different pathologies, such as diabesity, cardiovascular diseases and neurological disorders. All biochemical changes observed in MS, such as dysregulation in the glucose and lipid metabolism, immune response, endothelial cell function and intestinal microbiota, promote pathological bridges between metabolic syndrome, diabesity and cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disorders. This review aims to summarise metabolic syndrome's involvement in diabesity and highlight the link between MS and cardiovascular and neurological diseases. A better understanding of MS could promote a novel strategic approach to reduce MS comorbidities.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; diabesity; dysbiosis; gut microbiota; metabolic syndrome; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Strategies for Metabolic Syndrome: How Nutrition, Dietary Polyphenols, Physical Activity, and Lifestyle Modifications Address Diabesity, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Neurodegenerative Conditions.Metabolites. 2024 Jun 11;14(6):327. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060327. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38921462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Helicobacter pylori and metabolic syndrome on mast cell activation-related pathophysiology and neurodegeneration.Neurochem Int. 2024 May;175:105724. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105724. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Neurochem Int. 2024. PMID: 38508416 Review.
-
Gastrointestinal Disorders and Metabolic Syndrome: Dysbiosis as a Key Link and Common Bioactive Dietary Components Useful for their Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 13;21(14):4929. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144929. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32668581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic syndrome's new therapy: Supplement the gut microbiome.World J Diabetes. 2024 Apr 15;15(4):793-796. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.793. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38680700 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acid dysregulation, gut dysbiosis, and gastrointestinal cancer.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014 Nov;239(11):1489-504. doi: 10.1177/1535370214538743. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014. PMID: 24951470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perfluoroalkyl substances and metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional study using data from the US national health and nutrition examination survey.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 24;10(17):e36894. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36894. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281531 Free PMC article.
-
Association of metabolic syndrome and frailty with postoperative complications in older gastric cancer patients: A body composition perspective.Cancer Med. 2024 Sep;13(18):e70194. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70194. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39315666 Free PMC article.
-
Linking Metabolic Syndrome to Neurodegeneration Mechanisms and Potential Treatments.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr 24. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04947-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40272771 Review.
-
Relationship of weight-adjusted waist index and developmental disabilities in children 6 to 17 years of age: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 4;15:1406996. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1406996. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39027477 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Antioxidative Effects of Ginger and Cinnamon: A Comprehensive Review of Evidence and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Other Oxidative Stress-Related Disorders.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 25;13(4):392. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040392. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

