Proton Reirradiation for High-Risk Recurrent or New Primary Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38136268
- PMCID: PMC10742022
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15245722
Proton Reirradiation for High-Risk Recurrent or New Primary Breast Cancer
Abstract
Radiotherapy is an integral component of multidisciplinary breast cancer care. Given how commonly radiotherapy is used in the treatment of breast cancer, many patients with recurrences have received previous radiotherapy. Patients with new primary breast cancer may also have received previous radiotherapy to the thoracic region. Curative doses and comprehensive field photon reirradiation (reRT) have often been avoided in these patients due to concerns for severe toxicities to organs-at-risk (OARs), such as the heart, lungs, brachial plexus, and soft tissue. However, many patients may benefit from definitive-intent reRT, such as patients with high-risk disease features such as lymph node involvement and dermal/epidermal invasion. Proton therapy is a potentially advantageous treatment option for delivery of reRT due to its lack of exit dose and greater conformality that allow for enhanced non-target tissue sparing of previously irradiated tissues. In this review, we discuss the clinical applications of proton therapy for patients with breast cancer requiring reRT, the currently available literature and how it compares to historical photon reRT outcomes, treatment planning considerations, and questions in this area warranting further study. Given the dosimetric advantages of protons and the data reported to date, proton therapy is a promising option for patients who would benefit from the added locoregional disease control provided by reRT for recurrent or new primary breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; proton therapy; radiation therapy; reirradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
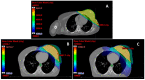
Figures
References
-
- Holleczek B., Stegmaier C., Radosa J.C., Solomayer E.-F., Brenner H. Risk of loco-regional recurrence and distant metastases of patients with invasive breast cancer up to ten years after diagnosis—Results from a registry-based study from Germany. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:520. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5710-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative G., Darby S., McGale P., Correa C., Taylor C., Arriagada R., Clarke M., Cutter D., Davies C., Ewertz M., et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378:1707–1716. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61629-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

