Prognostic Value of Circulating Cytokines in Chemorefractory Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 38136368
- PMCID: PMC10742027
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15245823
Prognostic Value of Circulating Cytokines in Chemorefractory Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
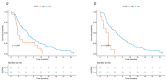
Circulating cytokines could be optimal biomarkers for prognostication and management decisions in colorectal cancer (CRC). Chemorefractory CRC patients with available plasma samples were included in this study. In the discovery cohort (n = 85), 182 circulating cytokines were tested with a semi-quantitative multiplex assay, and prognostic cytokines were analyzed in the validation cohort (n = 111) by ELISA. Overall survival (OS) was the primary outcome measure, with the false discovery rate (FDR) method (significance level of <0.01) being used to correct for multiple comparisons. Four cytokines were associated with OS in the discovery cohort: insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) (HR 2.1 [95%CI: 1.58-2.79], FDR < 0.001), insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) (HR 1.65 [95%CI: 1.28-2.13], FDR = 0.006), serum amyloid A (SAA) (HR 1.84 [95%CI: 1.39-2.43], FDR < 0.001), and angiotensin II (HR 1.65 [95%CI: 1.29-2.1], FDR = 0.006). Of these, IGFBP-1 (HR 2.70 [95%CI: 1.56-4.76], FDR = 0.007) and IGFBP-2 (HR 3.33 [95%CI: 1.64-6.67], FDR = 0.008) were confirmed to be independently associated with OS in the validation cohort. Patients with high concentrations of IGFBP-1 and/or IGFBP-2 had a median OS of 3.0 months as compared with 6.9 months for those with low concentrations of both cytokines (HR 2.44 [95%CI: 1.52-4.0], FDR = 0.002) Validation of circulating IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2 as independent prognostic biomarkers for chemorefractory CRC in larger, independent series is warranted.
Keywords: IGFBP-1; IGFBP-2; colorectal cancer; cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cremolini C., Loupakis F., Antoniotti C., Lupi C., Sensi E., Lonardi S., Mezi S., Tomasello G., Ronzoni M., Zaniboni A., et al. FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: Updated overall survival and molecular subgroup analyses of the open-label, phase 3 TRIBE study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1306–1315. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00122-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

