Random Lasers as Social Processes Simulators
- PMID: 38136481
- PMCID: PMC10742775
- DOI: 10.3390/e25121601
Random Lasers as Social Processes Simulators
Abstract
In this work, we suggest a quantum-like simulator concept to study social processes related to the solution of NP-hard problems. The simulator is based on the solaser model recently proposed by us in the framework of information cascade growth and echo chamber formation in social network communities. The simulator is connected with the random laser approach that we examine in the A and D-class (superradiant) laser limits. Novel network-enforced cooperativity parameters of decision-making agents, which may be measured as a result of the solaser simulation, are introduced and justified for social systems. The innovation diffusion in complex networks is discussed as one of the possible impacts of our proposal.
Keywords: complex networks; decision-making agents; innovation diffusion; quantum-like simulators; random lasers; superradiance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
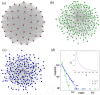
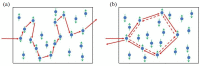
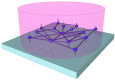

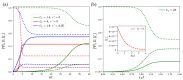
References
-
- Mohseni N., McMahon P., Byrnes T. Ising machines as hardware solvers of combinatorial optimization problems. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2022;4:363–379. doi: 10.1038/s42254-022-00440-8. - DOI
-
- Karp R.M. Reducibility among Combinatorial Problems. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 1972. pp. 85–103.
-
- Tanahashi K., Takayanagi S., Motohashi T., Tanaka S. Application of Ising Machines and a Software Development for Ising Machines. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2019;88:061010. doi: 10.7566/JPSJ.88.061010. - DOI
-
- Lucas A. Ising formulations of many NP problems. Front. Phys. 2014;2:5. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2014.00005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

