Melatonin as a Repairing Agent in Cadmium- and Free Fatty Acid-Induced Lipotoxicity
- PMID: 38136629
- PMCID: PMC10741790
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13121758
Melatonin as a Repairing Agent in Cadmium- and Free Fatty Acid-Induced Lipotoxicity
Abstract
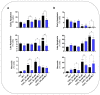
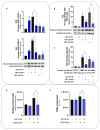
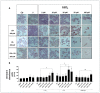
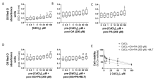
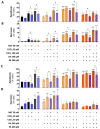
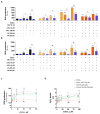
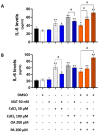
(1) Background: Cadmium (Cd) is a potentially toxic element with a long half-life in the human body (20-40 years). Cytotoxicity mechanisms of Cd include increased levels of oxidative stress and apoptotic signaling, and recent studies have suggested that these aspects of Cd toxicity contribute a role in the pathobiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a highly prevalent ailment associated with hepatic lipotoxicity and an increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In this study, Cd toxicity and its interplay with fatty acid (FA)-induced lipotoxicity have been studied in intestinal epithelium and liver cells; the cytoprotective function of melatonin (MLT) has been also evaluated. (2) Methods: human liver cells (HepaRG), primary murine hepatocytes and Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells were exposed to CdCl2 before and after induction of lipotoxicity with oleic acid (OA) and/or palmitic acid (PA), and in some experiments, FA was combined with MLT (50 nM) treatment. (3) Results: CdCl2 toxicity was associated with ROS induction and reduced cell viability in both the hepatic and intestinal cells. Cd and FA synergized to induce lipid droplet formation and ROS production; the latter was higher for PA compared to OA in liver cells, resulting in a higher reduction in cell viability, especially in HepaRG and primary hepatocytes, whereas CACO-2 cells showed higher resistance to Cd/PA-induced lipotoxicity compared to liver cells. MLT showed significant protection against Cd toxicity either considered alone or combined with FFA-induced lipotoxicity in primary liver cells. (4) Conclusions: Cd and PA combine their pro-oxidant activity to induce lipotoxicity in cellular populations of the gut-liver axis. MLT can be used to lessen the synergistic effect of Cd-PA on cellular ROS formation.
Keywords: cadmium; lipotoxicity; melatonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Farag A.M., Nimick D.A., Kimball B.A., Church S.E., Harper D.D., Brumbaugh W.G. Concentrations of metals in water, sediment, biofilm, benthic macroinvertebrates, and fish in the Boulder River watershed, Montana, and the role of colloids in metal uptake. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007;52:397–409. doi: 10.1007/s00244-005-0021-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chaumont A., De Winter F., Dumont X., Haufroid V., Bernard A. The threshold level of urinary cadmium associated with increased urinary excretion of retinol-binding protein and β2-microglobulin: A re-assessment in a large cohort of nickel-cadmium battery workers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011;68:257–264. doi: 10.1136/oem.2009.054122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pizzino G., Bitto A., Interdonato M., Galfo F., Irrera N., Mecchio A., Pallio G., Ramistella V., De Luca F., Minutoli L., et al. Oxidative stress and DNA repair and detoxification gene expression in adolescents exposed to heavy metals living in the Milazzo-Valle del Mela area (Sicily, Italy) Redox Biol. 2014;2:686–693. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.05.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

