Fluorescence-Based Mono- and Multimodal Imaging for In Vivo Tracking of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 38136656
- PMCID: PMC10742164
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13121787
Fluorescence-Based Mono- and Multimodal Imaging for In Vivo Tracking of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
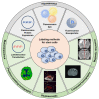
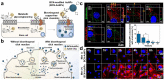
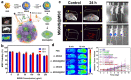
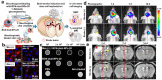
The advancement of stem cell therapy has offered transformative therapeutic outcomes for a wide array of diseases over the past decades. Consequently, stem cell tracking has become significant in revealing the mechanisms of action and ensuring safe and effective treatments. Fluorescence stands out as a promising choice for stem cell tracking due to its myriad advantages, including high resolution, real-time monitoring, and multi-fluorescence detection. Furthermore, combining fluorescence with other tracking modalities-such as bioluminescence imaging (BLI), positron emission tomography (PET), photoacoustic (PA), computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance (MR)-can address the limitations of single fluorescence detection. This review initially introduces stem cell tracking using fluorescence imaging, detailing various labeling strategies such as green fluorescence protein (GFP) tagging, fluorescence dye labeling, and nanoparticle uptake. Subsequently, we present several combinations of strategies for efficient and precise detection.
Keywords: fluorescence imaging; in vivo cell imaging; multimodal imaging; stem cell tracking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Complementary early-phase magnetic particle imaging and late-phase positron emission tomography reporter imaging of mesenchymal stem cells in vivo.Nanoscale. 2023 Feb 16;15(7):3408-3418. doi: 10.1039/d2nr03684c. Nanoscale. 2023. PMID: 36722918
-
Real-time tracking of adipose tissue-derived stem cells with injectable scaffolds in the infarcted heart.Heart Vessels. 2013 May;28(3):385-96. doi: 10.1007/s00380-012-0275-0. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Heart Vessels. 2013. PMID: 22940832
-
Tracking Neural Stem Cells in vivo: Achievements and Limitations.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Jun;18(5):1774-1788. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10333-z. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 35122628 Review.
-
Magnetic resonance and photoacoustic imaging of brain tumor mediated by mesenchymal stem cell labeled with multifunctional nanoparticle introduced via carotid artery injection.Nanotechnology. 2018 Apr 20;29(16):165101. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aaaf16. Nanotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29438105 Free PMC article.
-
19 F MRI Probes for Multimodal Imaging.Chemistry. 2022 Jan 24;28(5):e202102556. doi: 10.1002/chem.202102556. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Chemistry. 2022. PMID: 34705306 Review.
Cited by
-
An update on recent advances in fluorescent materials for fluorescence molecular imaging: a review.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 30;15(28):22267-22284. doi: 10.1039/d5ra03102h. eCollection 2025 Jun 30. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40599579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Female Infertility Treatment: Protocols and Preliminary Results.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 13;14(9):1161. doi: 10.3390/life14091161. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Quantum Yields and Biomedical Fluorescent Imaging Applications of Photosensitized Trivalent Lanthanide Ion-Based Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 24;25(21):11419. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111419. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual/Multi-Modal Image-Guided Diagnosis and Therapy Based on Luminogens with Aggregation-Induced Emission.Molecules. 2024 Jan 11;29(2):371. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020371. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intramyocardial injection of pre-cultured endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells inside alginate/gelatin microspheres induced angiogenesis in infarcted rabbits.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jun 12;23(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02301-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40506721 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

