NUP85 as a Neurodevelopmental Gene: From Podocyte to Neuron
- PMID: 38136965
- PMCID: PMC10743110
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14122143
NUP85 as a Neurodevelopmental Gene: From Podocyte to Neuron
Abstract
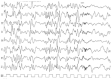
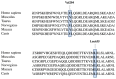
Pathogenic gene variants encoding nuclear pore complex (NPC) proteins were previously implicated in the pathogenesis of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). The NUP85 gene, encoding nucleoporin, is related to a very rare form of SRNS with limited genotype-phenotype information. We identified an Italian boy affected with an SRNS associated with severe neurodevelopmental impairment characterized by microcephaly, axial hypotonia, lack of achievement of motor milestones, and refractory seizures with an associated hypsarrhythmic pattern on electroencephalography. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed hypoplasia of the corpus callosum and a simplified gyration of the cerebral cortex. Since the age of 3 years, the boy was followed up at our Pediatric Nephrology Department for an SRNS, with a focal segmental glomerulosclerosis at renal biopsy. The boy died 32 months after SRNS onset, and a Whole-Exome Sequencing analysis revealed a novel compound heterozygous variant in NUP85 (NM_024844.5): 611T>A (p.Val204Glu), c.1904T>G (p.Leu635Arg), inherited from the father and mother, respectively. We delineated the clinical phenotypes of NUP85-related disorders, reviewed the affected individuals so far reported in the literature, and overall expanded both the phenotypic and the molecular spectrum associated with this ultra-rare genetic condition. Our study suggests a potential occurrence of severe neurological phenotypes as part of the NUP85-related clinical spectrum and highlights an important involvement of nucleoporin in brain developmental processes and neurological function.
Keywords: NUP85; developmental delay; epileptic spasm; microcephaly; nephrotic syndrome type 17; steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Trautmann A., Vivarelli M., Samuel S., Gipson D., Sinha A., Schaefer F., Hui N.K., Boyer O., Saleem M.A., Feltran L., et al. IPNA clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020;35:1529–1561. doi: 10.1007/s00467-020-04519-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manole A., Efthymiou S., O’connor E., Mendes M.I., Jennings M., Maroofian R., Davagnanam I., Mankad K., Lopez M.R., Salpietro V., et al. De Novo and Bi-allelic Pathogenic Variants in NARS1 Cause Neurodevelopmental Delay Due to Toxic Gain-of-Function and Partial Loss-of-Function Effects. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020;107:311–324. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.06.016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

