Computational Characterization of Undifferentially Expressed Genes with Altered Transcription Regulation in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 38136991
- PMCID: PMC10742656
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14122169
Computational Characterization of Undifferentially Expressed Genes with Altered Transcription Regulation in Lung Cancer
Abstract
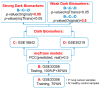
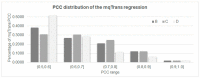
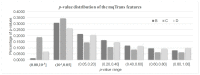
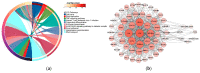
A transcriptome profiles the expression levels of genes in cells and has accumulated a huge amount of public data. Most of the existing biomarker-related studies investigated the differential expression of individual transcriptomic features under the assumption of inter-feature independence. Many transcriptomic features without differential expression were ignored from the biomarker lists. This study proposed a computational analysis protocol (mqTrans) to analyze transcriptomes from the view of high-dimensional inter-feature correlations. The mqTrans protocol trained a regression model to predict the expression of an mRNA feature from those of the transcription factors (TFs). The difference between the predicted and real expression of an mRNA feature in a query sample was defined as the mqTrans feature. The new mqTrans view facilitated the detection of thirteen transcriptomic features with differentially expressed mqTrans features, but without differential expression in the original transcriptomic values in three independent datasets of lung cancer. These features were called dark biomarkers because they would have been ignored in a conventional differential analysis. The detailed discussion of one dark biomarker, GBP5, and additional validation experiments suggested that the overlapping long non-coding RNAs might have contributed to this interesting phenomenon. In summary, this study aimed to find undifferentially expressed genes with significantly changed mqTrans values in lung cancer. These genes were usually ignored in most biomarker detection studies of undifferential expression. However, their differentially expressed mqTrans values in three independent datasets suggested their strong associations with lung cancer.
Keywords: bioinformatics; dark biomarker; differential expression; lung cancer; mqTrans; transcription regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Alberg A.J., Samet J.M. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Chest. 2008;3:592. - PubMed
-
- Gainor J.F., Tan D., Pas T.D., Solomon B.J., Ahmad A., Lazzari C., Marinis F.D., Spitaleri G., Schultz K., Friboulet L. Progression-Free and Overall Survival in ALK-Positive NSCLC Patients Treated with Sequential Crizotinib and Ceritinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;21:2745–2752. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 20210509055RQ/Senior and Junior Technological Innovation Team
- ZK2023-297/Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Projects
- gzwkj2023-565/Science and Technology Foundation of Health Commission of Guizhou Province
- JJKH20220245KJ and JJKH20220226SK/Science and Technology Project of Education Department of Jilin Province
- 62072212 and U19A2061/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

