Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Isoquinoline Alkaloid Biosynthesis of Coptis chinensis in Different Years
- PMID: 38137054
- PMCID: PMC10742649
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14122232
Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Isoquinoline Alkaloid Biosynthesis of Coptis chinensis in Different Years
Abstract
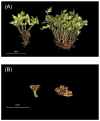
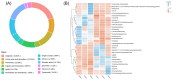
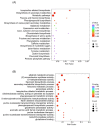
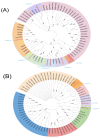
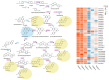
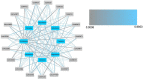
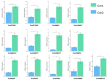
Coptis chinensis is a perennial herb of the Ranunculaceae family. The isoquinoline alkaloid is the main active component of C. chinensis, mainly exists in its rhizomes and has high clinical application potential. The in vitro synthesis of isoquinoline alkaloids is difficult because their structures are complex; hence, plants are still the main source of them. In this study, two-year and four-year rhizomes of C. chinensis were selected to investigate the effect of growth years on the accumulation of isoquinoline alkaloids. Two-year and four-year C. chinensis were selected for metabolomics detection and transcriptomic analysis. A total of 413 alkaloids were detected by metabolomics analysis, of which 92 were isoquinoline alkaloids. (S)-reticuline was a significantly different accumulated metabolite of the isoquinoline alkaloids biosynthetic pathway in C. chinensis between the two groups. The results of transcriptome analysis showed that a total of 464 differential genes were identified, 36 of which were associated with the isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis pathway of C. chinensis. Among them, 18 genes were correlated with the content of important isoquinoline alkaloids. Overall, this study provided a comprehensive metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of the rapid growth stage of C. chinensis rhizome from the perspective of growth years. It brought new insights into the biosynthetic pathway of isoquinoline alkaloids and provided information for utilizing biotechnology to improve their contents in C. chinensis.
Keywords: Coptis chinensis; RNA-Seq; UPLC-MS/MS; biosynthesis; isoquinoline alkaloids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals cadmium exposure enhanced the isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis and disease resistance in Coptis chinensis.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Feb;271:115940. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.115940. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 38218103
-
Full-length transcriptome analysis of Coptis deltoidea and identification of putative genes involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloids biosynthesis based on combined sequencing platforms.Plant Mol Biol. 2020 Mar;102(4-5):477-499. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00959-y. Epub 2020 Jan 4. Plant Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31902069
-
Effects of growing Coptis chinensis Franch in the natural understory vs. under a manmade scaffold on its growth, alkaloid contents, and rhizosphere soil microenvironment.PeerJ. 2022 Jul 20;10:e13676. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13676. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35880218 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on medicinal resources of Coptis and its isoquinoline alkaloids].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jul;46(14):3504-3513. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210430.103. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34402272 Review. Chinese.
-
Coptis Chinensis Franch: Substance Basis, Mechanism of Action and Quality Control Standard Revealed Based on the Q-marker Concept and New Strategy of Systemic Pharmacology and Biosynthesis Research.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(23):2013-2032. doi: 10.2174/0115680266305274240723120426. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39136504 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined analysis of the metabolome and transcriptome reveals the metabolic characteristics and candidate genes involved in alkaloid metabolism in Heuchera micrantha Douglas ex Lindl.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 6;24(1):639. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05363-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38971732 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Investigation on Two Different Seaweeds Under Arsenic Exposure.Foods. 2024 Dec 16;13(24):4055. doi: 10.3390/foods13244055. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39766997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee H.S., Kang D.G., Shon E.J., Oh H. Antihypertensive effects of the main components of Coptis chinensis Franch. FASEB J. 2002;16:A496.
-
- Zhong G.Y., Huang X.P., Ma K.S., Chen S.J., Qin S.Y. Quality assessment of Coptis chinensis in China. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China J. Chin. Mater. Medica. 2005;30:495–497. - PubMed
-
- Wang D.-Q., Peng H.-S. The vicissitude of the historically famous medicinal herb Xuan Huanglian (Coptis chinensis var. brevisepala) Zhonghua Yi Shi Za Zhi. 2008;38:137–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

