A Next-Generation Sequencing Study in a Cohort of Sicilian Patients with Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 38137339
- PMCID: PMC10740523
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11123118
A Next-Generation Sequencing Study in a Cohort of Sicilian Patients with Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
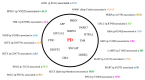
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a multisystem and multifactorial disorder and, therefore, the application of modern genetic techniques may assist in unraveling its complex pathophysiology. We conducted a clinical-demographic evaluation of 126 patients with PD, all of whom were Caucasian and of Sicilian ancestry. DNA was extracted from the peripheral blood for each patient, followed by sequencing using a Next-Generation Sequencing system. This system was based on a custom gene panel comprising 162 genes. The sample underwent further filtering, taking into account the allele frequencies of genetic variants, their presence in the Human Gene Mutation Database, and their association in the literature with PD or other movement/neurodegenerative disorders. The largest number of variants was identified in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) gene. However, variants in other genes, such as acid beta-glucosidase (GBA), DNA polymerase gamma catalytic subunit (POLG), and parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (PRKN), were also discovered. Interestingly, some of these variants had not been previously associated with PD. Enhancing our understanding of the genetic basis of PD and identifying new variants possibly linked to the disease will contribute to improved diagnostic accuracy, therapeutic developments, and prognostic insights for affected individuals.
Keywords: NGS; Parkinson’s disease; gene variants; movement disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Angela Cordella was employed by the company Genomix4Life Srl. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Iwaki H., Blauwendraat C., Leonard H.L., Liu G., Maple-Grødem J., Corvol J.-C., Pihlstrøm L., van Nimwegen M., Hutten S.J., Nguyen K.-D.H., et al. Genetic Risk of Parkinson Disease and Progression: An Analysis of 13 Longitudinal Cohorts. Neurol. Genet. 2019;5:e348. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000348. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

