Effect of Vancomycin, Gentamicin and Clindamycin on Cartilage Cells In Vitro
- PMID: 38137364
- PMCID: PMC10740484
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11123143
Effect of Vancomycin, Gentamicin and Clindamycin on Cartilage Cells In Vitro
Abstract
Background: The treatment of grafts with vancomycin for ligament reconstruction in knee surgery is the current standard. However, high antibiotic concentrations have chondrotoxic effects.
Purpose: To test the chondrotoxicity of clindamycin, gentamicin and vancomycin in comparable concentrations. In vitro and in vivo effective concentrations hugely vary from drug to drug. To allow for comparisons between these three commonly used antibiotics, the concentration ranges frequently used in orthopedic surgical settings were tested.
Study design: Controlled laboratory study.
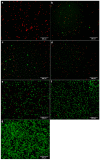
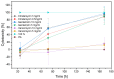
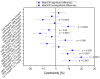
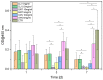
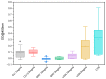
Methods: Human cartilage from 10 specimens was used to isolate chondrocytes. The chondrocytes were treated with clindamycin (1 mg/mL and 0.5 mg/mL), gentamicin (10 mg/mL and 5 mg/mL) or vancomycin (10 mg/mL and 5 mg/mL), at concentrations used for preoperative infection prophylaxis in ligament surgery. Observations were taken over a period of 7 days. A control of untreated chondrocytes was included. To test the chondrotoxicity, a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) test and a water-soluble tetrazolium salt (WST-1) assay were performed on days 1, 3 and 7. In addition, microscopic examinations were performed after fluorescence staining of the cells at the same time intervals.
Results: All samples showed a reasonable vitality of the cartilage cells after 72 h. However, clindamycin and gentamicin both showed higher chondrotoxicity in all investigations compared to vancomycin. After a period of 7 days, only chondrocytes treated with vancomycin showed reasonable vitality.
Conclusions: The preoperative treatment of ligament grafts with vancomycin is the most reasonable method for infection prophylaxis, in accordance with the current study results regarding chondrotoxicity; however, clindamycin and gentamicin cover a wider anti-bacterial spectrum.
Clinical relevance: The prophylactic antibiotic treatment of ligament grafts at concentrations of 5 mg/mL or 10 mg/mL vancomycin is justifiable and reasonable. In specific cases, even the use of gentamicin and clindamycin is appropriate.
Keywords: LDH test; Live Dead staining; WST-1 test; chondrotoxicity of antibiotics; concentration of antibiotics; infection prophylaxis; ligament surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vancomycin Concentrations in Synovial Fluid Do Not Reach Chondrotoxic Thresholds After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction With Vancomycin-Soaked Autologous Soft Tissue Grafts: An In Vivo Prospective Observational Study in Humans.Am J Sports Med. 2023 Jun;51(7):1715-1720. doi: 10.1177/03635465231169040. Epub 2023 May 10. Am J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 37161935 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison Between Vancomycin and Gentamicin for Intraoperative Presoaking of Hamstring Graft in Primary Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction.Cureus. 2022 Feb 23;14(2):e22550. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22550. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35345679 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Site Infection After Arthroplasty: Comparative Effectiveness of Prophylactic Antibiotics: Do Surgical Care Improvement Project Guidelines Need to Be Updated?J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014 Jun 18;96(12):970-977. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.M.00663. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014. PMID: 24951731
-
Review of Intra-Articular Use of Antibiotics and Antiseptic Irrigation and Their Systematic Association with Chondrolysis.Kans J Med. 2023 Oct 30;16(3):272-276. doi: 10.17161/kjm.vol16.20357. eCollection 2023. Kans J Med. 2023. PMID: 37954883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AUA-recommended Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Primary Penile Implantation Results in a Higher, Not Lower, Risk for Postoperative Infection: A Multicenter Analysis.J Urol. 2023 Feb;209(2):399-409. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000003071. Epub 2022 Nov 16. J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36383789 Review.
Cited by
-
The in vitro elution characteristics of vancomycin from the ligament augmentation and reconstruction system.J Exp Orthop. 2024 Dec 3;11(4):e70104. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70104. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Exp Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39629194 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Three Kayviruses Against Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from COVID-19 Patients.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Mar 3;14(3):257. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14030257. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashoobi M.T., Asgary M.R., Sarafi M., Fathalipour N., Pirooz A., Jafaryparvar Z., Rafiei E., Farzin M., Samidoust P., Delshad M.S.E. Incidence rate and risk factors of surgical wound infection in general surgery patients: A cross-sectional study. Int. Wound J. 2023;20:2640–2648. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14137. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tiri B., Bruzzone P., Priante G., Sensi E., Costantini M., Vernelli C., Martella L.A., Francucci M., Andreani P., Mariottini A., et al. Impact of antimicrobial stewardship interventions on appropriateness of surgical antibiotic prophylaxis: How to improve. Antibiotics. 2020;9:168. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9040168. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

