Prefrontal Dopamine in Flexible Adaptation to Environmental Changes: A Game for Two Players
- PMID: 38137410
- PMCID: PMC10740496
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11123189
Prefrontal Dopamine in Flexible Adaptation to Environmental Changes: A Game for Two Players
Abstract
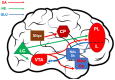
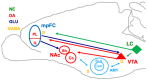
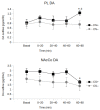
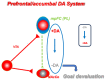
Deficits in cognitive flexibility have been characterized in affective, anxiety, and neurodegenerative disorders. This paper reviews data, mainly from studies on animal models, that support the existence of a cortical-striatal brain circuit modulated by dopamine (DA), playing a major role in cognitive/behavioral flexibility. Moreover, we reviewed clinical findings supporting misfunctioning of this circuit in Parkinson's disease that could be responsible for some important non-motoric symptoms. The reviewed findings point to a role of catecholaminergic transmission in the medial prefrontal cortex (mpFC) in modulating DA's availability in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), as well as a role of NAc DA in modulating the motivational value of natural and conditioned stimuli. The review section is accompanied by a preliminary experiment aimed at testing weather the extinction of a simple Pavlovian association fosters increased DA transmission in the mpFC and inhibition of DA transmission in the NAc.
Keywords: dopamine; extinction; goal-directed; medial prefrontal cortex; nucleus accumbens; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Basolateral amygdala modulation of the nucleus accumbens dopamine response to stress: role of the medial prefrontal cortex.Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Mar;17(6):1287-95. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02560.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12670317
-
Lesion of medial prefrontal dopamine terminals abolishes habituation of accumbens shell dopamine responsiveness to taste stimuli.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Feb;37(4):613-22. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12068. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23216547
-
S-(N, N-diethylcarbamoyl)glutathione (carbamathione), a disulfiram metabolite and its effect on nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex dopamine, GABA, and glutamate: a microdialysis study.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23891816 Free PMC article.
-
Habituation of the responsiveness of mesolimbic and mesocortical dopamine transmission to taste stimuli.Front Integr Neurosci. 2014 Mar 4;8:21. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2014.00021. eCollection 2014. Front Integr Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24624065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in motivated behavior: a unifying interpretation with special reference to reward-seeking.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999 Dec;31(1):6-41. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(99)00023-5. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999. PMID: 10611493 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Dopamine in Neurological, Psychiatric, and Metabolic Disorders and Cancer: A Complex Web of Interactions.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 17;13(2):492. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020492. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002905 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol, flexible behavior, and the prefrontal cortex: Functional changes underlying impaired cognitive flexibility.Neuropharmacology. 2024 Dec 1;260:110114. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.110114. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39134298 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

