A-Type Natriuretic Peptide Alters the Impact of Azithromycin on Planktonic Culture and on (Monospecies and Binary) Biofilms of Skin Bacteria Kytococcus schroeteri and Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 38138110
- PMCID: PMC10746058
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11122965
A-Type Natriuretic Peptide Alters the Impact of Azithromycin on Planktonic Culture and on (Monospecies and Binary) Biofilms of Skin Bacteria Kytococcus schroeteri and Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
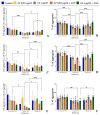
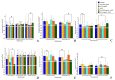
It has been established that the human atrial natriuretic peptide is able to alter the effect of azithromycin on Kytococcus schroeteri H01 and Staphylococcus aureus 209P monospecies and binary biofilms. The effect of the hormone depends on the surface type and cultivation system, and it may have both enhancing and counteracting effects. The antagonistic effect of the hormone was observed mostly on hydrophobic surfaces, whereas the additive effect was observed on hydrophilic surfaces like glass. Also, the effect of the hormone depends on the antibiotic concentration and bacterial species. The combination of azithromycin and ANP led to an amplification of cell aggregation in biofilms, to the potential increase in matrix synthesis, and to a decrease in S. aureus in the binary community. Also, ANP, azithromycin, and their combinations caused the differential expression of genes of resistance to different antibiotics, like macrolides (mostly increasing expression in kytococci), fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, and others, in both bacteria.
Keywords: Kytococcus schroeteri; Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotics; atrial natriuretic peptides; azithromycin; biofilms; hormones; human skin microbiota; multispecies biofilms.
Conflict of interest statement
Miss Aleksandra S. Novikova as an employee of LLC “Bavar+” on behalf of LLC “Bavar+” declares no conflict of interests. Other academic authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Regulation of Monospecies and Mixed Biofilms Formation of Skin Staphylococcus aureus and Cutibacterium acnes by Human Natriuretic Peptides.Front Microbiol. 2018 Dec 10;9:2912. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02912. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30619105 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Affects Skin Commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis and Cutibacterium acnes Dual-Species Biofilms.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 8;9(3):552. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030552. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33800171 Free PMC article.
-
Silver nanoparticles as a bioadjuvant of antibiotics against biofilm-mediated infections with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic rhinosinusitis patients.Pathology. 2022 Jun;54(4):453-459. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2021.08.014. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Pathology. 2022. PMID: 34844745
-
Endocarditis due to Kytococcus schroeteri: case report and review of the literature.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Mar;44(3):1187-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.3.1187-1189.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16517928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Periprosthetic joint infection caused by kytococcus schroeteri: The first reported case and a review of the literature.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2023 May;106(1):115922. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2023.115922. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36933454 Review.
References
-
- Wang B., Yao M., Lv L., Ling Z., Li L. The human microbiota in health and disease. Engineering. 2017;3:71–82. doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2017.01.008. - DOI
-
- Boukerb A.M., Robert M., Teteneva N.A., Danilova N.D., Zhurina M.V., Mart’yanov S.V., Plakunov V.K., Feuilloley M.G.J., Gannesen A.V. Draft genome sequence of Kytococcus schroeteri strain h01, isolated from human skin. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019;8:e01081-19. doi: 10.1128/MRA.01081-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

