Acute Exercise Promptly Normalizes Myocardial Myosin Heavy-Chain Isoform mRNA Composition in Diabetic Rats: Implications for Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 38138296
- PMCID: PMC10744754
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59122193
Acute Exercise Promptly Normalizes Myocardial Myosin Heavy-Chain Isoform mRNA Composition in Diabetic Rats: Implications for Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
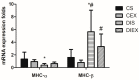
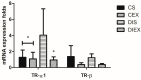
Background and Objectives: The acute effects of exercise on the myosin heavy-chain (MHC) isoform mRNA expression and the upstream transcription factors in diabetic and non-diabetic hearts remain unexplored. We aimed to determine the acute effect of a single exercise session on the expression of left ventricular MHC, MHC-α and MHC-β, and thyroid receptor (TR), TR-α1 and TR-β, isoform mRNA in diabetic and non-diabetic rats. Materials and Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were assigned to four groups: non-diabetic control (CS), diabetic exercise (DIEX), sedentary diabetic (DIS), and non-diabetic exercise (CEX). Diabetes was induced via streptozotocin injection (55 mg/kg). DIEX and CEX rats performed an exercise session (60 min at 50 m/min and 0% grade) 6-7 weeks after diabetes induction. Results: MHC-α mRNA was lower in DIS (p = 0.03) and not different in DIEX (p = 0.1) relative to CS. DIS showed higher MHC-β mRNA than the non-diabetic rats, CS and CEX (p = 0.02 and p = 0.009, respectively). MHC-β mRNA in DIEX was normalized to non-diabetic levels in CS (p = 0.3). TR-α1 was higher in DIS and not different in DIEX relative to CS and CEX (p = 0.03 and p = 1.0, respectively). In CEX, exercise did not change MHC-α, MHC-β, and TR-α1 relative to CS (p = 1.0). TR-β was not different between groups. Conclusion: In conclusion, exercise appears to acutely normalize the myocardial MHC and TR isoform mRNA expression only in the diabetic heart. These responses may induce therapeutic mechanisms other than changing the MHC isoform composition.
Keywords: exercise training; myocardium; myosin isozymes; sedentary lifestyle; thyroid receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest or any disclosure to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in myocardial myosin heavy chain isoform composition with exercise and post-exercise cold-water immersion.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2021 Jun;42(2):183-191. doi: 10.1007/s10974-021-09603-z. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2021. PMID: 33826086
-
Effects of exercise training and diabetes on cardiac myosin heavy chain composition.Mol Cell Biochem. 1992 Nov 18;117(2):175-9. doi: 10.1007/BF00230757. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1488051
-
Exercise training improves cardiac function-related gene levels through thyroid hormone receptor signaling in aged rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004 May;286(5):H1696-705. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00761.2003. Epub 2004 Jan 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14704232
-
Post-myocardial infarction exercise training beneficially regulates thyroid hormone receptor isoforms.J Physiol Sci. 2018 Nov;68(6):743-748. doi: 10.1007/s12576-017-0587-z. Epub 2017 Dec 22. J Physiol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29273887 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial retinoid X receptor, thyroid hormone receptor, and myosin heavy chain gene expression in the rat during adult aging.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999 Jan;54(1):B23-7. doi: 10.1093/gerona/54.1.b23. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999. PMID: 10026651
Cited by
-
Endurance exercise attenuates Gαq-RNAi induced hereditary obesity and skeletal muscle dysfunction via improving skeletal muscle Srl/MRCC-I pathway in Drosophila.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 15;14(1):28207. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79415-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39548180 Free PMC article.
-
MAP Kinase Phosphatase-5 Deficiency Improves Endurance Exercise Capacity.Cells. 2025 Mar 11;14(6):410. doi: 10.3390/cells14060410. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40136658 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

