Spherical Polyelectrolyte Brushes as Flocculants and Retention Aids in Wet-End Papermaking
- PMID: 38138474
- PMCID: PMC10745445
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28247984
Spherical Polyelectrolyte Brushes as Flocculants and Retention Aids in Wet-End Papermaking
Abstract
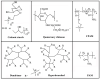
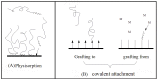
As the criteria of energy conservation, emission reduction, and environmental protection become more important, and with the development of wet-end papermaking, developing excellent retention aids is of great significance. Spherical polyelectrolyte brushes (SPBs) bearing polyelectrolyte chains grafted densely to the surface of core particle have the potential to be novel retention aids in wet-end papermaking not only because of their spherical structure, but also due to controllable grafting density and molecular weight. Such characteristics are crucial in order to design multi-functional retention aids in sophisticated papermaking systems. This review presents some important recent advances with respect to retention aids, including single-component system and dual-component systems. Then, basic theory in papermaking is also briefly reviewed. Based on these advances, it emphatically describes spherical polyelectrolyte brushes, focused on their preparation methods, characterization, conformation, and applications in papermaking. This work is expected to contribute to improve a comprehensive understanding on the composition, properties, and function mechanisms of retention aids, which helps in the further investigation on the design of novel retention aids with excellent performance.
Keywords: flocculation; retention aids; spherical polyelectrolyte brushes; wet-end papermaking.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Ma H. A review of ways to adjust papermaking wet-end chemistry: Manipulation of cellulosic colloidal behavior. Lignocellulose. 2014;3:69–107.
-
- Gibbs A., Pelton R., Cong R. The influence of dextran derivatives on polyethylene oxide and polyacrylamide-induced calcium carbonate flocculation and floc strength. Colloids Surf. A. 1999;159:31–35. doi: 10.1016/S0927-7757(99)00160-0. - DOI
-
- Lima D.U., Oliveira R.C., Buckeridge M.C. Seed storage hemicelluloses as wet-end additives in papermaking. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003;52:367–373. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00008-0. - DOI
-
- Fatemeh N., Hamidreza R., Hossein R., Hossein J.T. Application of bio-based modified kaolin clay engineered as papermaking additive for improving the properties of filled recycled papers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019;182:105258.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

