Neuroprotective Effects of Aldehyde-Reducing Composition in an LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation Model of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 38138478
- PMCID: PMC10745824
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28247988
Neuroprotective Effects of Aldehyde-Reducing Composition in an LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation Model of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
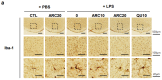
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a complex neurodegenerative disease in which neuroinflammation and oxidative stress interact to contribute to pathogenesis. This study investigates the in vivo neuroprotective effects of a patented yeast extract lysate in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation model. The yeast extract lysate, named aldehyde-reducing composition (ARC), exhibited potent antioxidant and anti-aldehyde activities in vitro. Oral administration of ARC at 10 or 20 units/kg/day for 3 days prior to intraperitoneal injection of LPS (10 mg/kg) effectively preserved dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) and striatum by preventing LPS-induced cell death. ARC also normalized the activation of microglia and astrocytes in the SN, providing further evidence for its neuroprotective properties. In the liver, ARC downregulated the LPS-induced increase in inflammatory cytokines and reversed the LPS-induced decrease in antioxidant-related genes. These findings indicate that ARC exerts potent antioxidant, anti-aldehyde, and anti-inflammatory effects in vivo, suggesting its potential as a disease-modifying agent for the prevention and treatment of neuroinflammation-related diseases, including Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: ALDH; Parkinson’s disease; neuroinflammation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Sora Kang, Youngjin Noh and Hung Taeck Kwon come from the company Picoentech Co., Ltd. The authors declare no conflict of interest other than the patent mentioned above.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Mechanisms of GTS-21, an α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonist, in Neuroinflammation and Parkinson's Disease Mouse Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 16;23(8):4420. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084420. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457238 Free PMC article.
-
Erinacine A Prevents Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Glial Cell Activation to Protect Dopaminergic Neurons against Inflammatory Factor-Induced Cell Death In Vitro and In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 12;23(2):810. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020810. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054997 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of endotoxin tolerance on peripheral lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and dopaminergic neuronal injury.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022 Jun;44(3):326-337. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2043900. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022. PMID: 35260024
-
Advances in NURR1-Regulated Neuroinflammation Associated with Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 19;23(24):16184. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416184. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective strategies in Parkinson's disease using the models of 6-hydroxydopamine and MPTP.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;899:262-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06192.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 10863545 Review.
Cited by
-
A Compound Containing Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Relieves the Effects of Alcohol Consumption and Hangover Symptoms in Healthy Men: An Open-Labeled Comparative Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 20;17(8):1087. doi: 10.3390/ph17081087. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204192 Free PMC article.
-
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Toxic Models of Parkinsonism.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 31;26(3):1248. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031248. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel yeast-derived aldehyde-reducing compound MF001 protects against alcohol-induced liver damage.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 10;20(7):e0327648. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327648. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40638641 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

