Epimerisation in Peptide Synthesis
- PMID: 38138507
- PMCID: PMC10745333
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28248017
Epimerisation in Peptide Synthesis
Abstract
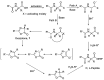
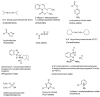
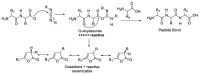
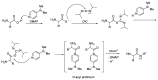
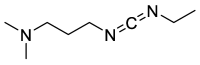
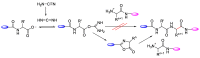
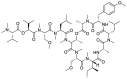
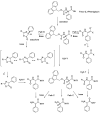
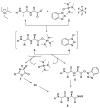
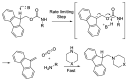
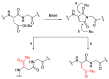
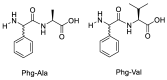
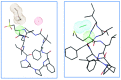
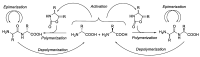
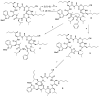
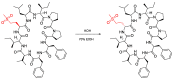
Epimerisation is basically a chemical conversion that includes the transformation of an epimer into another epimer or its chiral partner. Epimerisation of amino acid is a side reaction that sometimes happens during peptide synthesis. It became the most avoided reaction because the process affects the overall conformation of the molecule, eventually even altering the bioactivity of the peptide. Epimerised products have a high similarity of physical characteristics, thus making it difficult for them to be purified. In regards to amino acids, epimerisation is very important in keeping the chirality of the assembled amino acids unchanged during the peptide synthesis and obtaining the desirable product without any problematic purification. In this review, we report several factors that induce epimerisation during peptide synthesis, including how to characterise and affect the bioactivities. To avoid undesirable epimerisation, we also describe several methods of suppressing the process.
Keywords: cyclisation; epimerisation; peptide synthesis; side reaction; solid-phase peptide synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

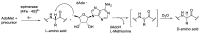
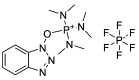
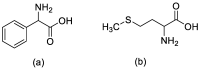
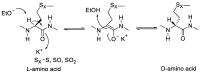
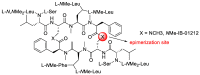



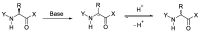
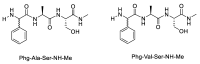
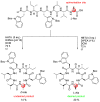

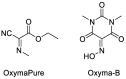
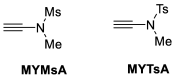




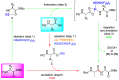

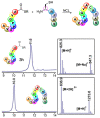
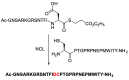


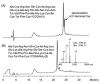
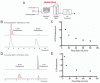
References
-
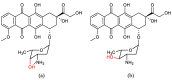
- Heck S.D., Siok C.J., Krapcho K.J., Kelbaugh P.R., Thadeio P.F., Welch M.J., Williams R.D., Ganong A.H., Kelly M.E., Lanzetti A.J., et al. Functional consequences of posttranslational isomerization of Ser46 in a calcium channel toxin. Science. 1994;266:1065–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.7973665. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

