The Discovery of Indole-2-carboxylic Acid Derivatives as Novel HIV-1 Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors
- PMID: 38138510
- PMCID: PMC10745497
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28248020
The Discovery of Indole-2-carboxylic Acid Derivatives as Novel HIV-1 Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors
Abstract
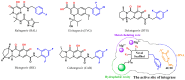
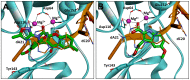
As an important antiviral target, HIV-1 integrase plays a key role in the viral life cycle, and five integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) have been approved for the treatment of HIV-1 infections so far. However, similar to other clinically used antiviral drugs, resistance-causing mutations have appeared, which have impaired the efficacy of INSTIs. In the current study, to identify novel integrase inhibitors, a set of molecular docking-based virtual screenings were performed, and indole-2-carboxylic acid was developed as a potent INSTI scaffold. Indole-2-carboxylic acid derivative 3 was proved to effectively inhibit the strand transfer of HIV-1 integrase, and binding conformation analysis showed that the indole core and C2 carboxyl group obviously chelated the two Mg2+ ions within the active site of integrase. Further structural optimizations on compound 3 provided the derivative 20a, which markedly increased the integrase inhibitory effect, with an IC50 value of 0.13 μM. Binding mode analysis revealed that the introduction of a long branch on C3 of the indole core improved the interaction with the hydrophobic cavity near the active site of integrase, indicating that indole-2-carboxylic acid is a promising scaffold for the development of integrase inhibitors.
Keywords: HIV-1 integrase; design and synthesis; indole-2-carboxylic acid; structural optimization; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of indole-2-carboxylic acid derivatives as novel HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2024 Mar 18;14(13):9020-9031. doi: 10.1039/d3ra08320a. eCollection 2024 Mar 14. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38500630 Free PMC article.
-
In-Silico docking of HIV-1 integrase inhibitors reveals a novel drug type acting on an enzyme/DNA reaction intermediate.Retrovirology. 2007 Mar 20;4:21. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-4-21. Retrovirology. 2007. PMID: 17374162 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 4-Oxo-4,10-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylic Acid Derivatives as HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Docking Studies, Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Biological Activities.Med Chem. 2021;17(9):1060-1071. doi: 10.2174/1573406416666200909104616. Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32901587
-
Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors Are Effective Anti-HIV Drugs.Viruses. 2021 Jan 29;13(2):205. doi: 10.3390/v13020205. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33572956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Close-up: HIV/SIV intasome structures shed new light on integrase inhibitor binding and viral escape mechanisms.FEBS J. 2021 Jan;288(2):427-433. doi: 10.1111/febs.15438. Epub 2020 Jun 22. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 32506843 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors and the Capsid Inhibitor Lenacapavir against HIV-2, and Exploring the Effect of Raltegravir on the Activity of SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2024 Oct 13;16(10):1607. doi: 10.3390/v16101607. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459940 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of raltegravir analogs to enhance inhibitory efficiency against HIV integrase.Sci Rep. 2025 May 13;15(1):16665. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01666-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40360594 Free PMC article.
-
Indole Derivatives: A Versatile Scaffold in Modern Drug Discovery-An Updated Review on Their Multifaceted Therapeutic Applications (2020-2024).Molecules. 2024 Oct 9;29(19):4770. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194770. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

