Non-Destructive Characterization of Cured-in-Place Pipe Defects
- PMID: 38138712
- PMCID: PMC10745074
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16247570
Non-Destructive Characterization of Cured-in-Place Pipe Defects
Abstract
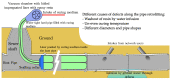
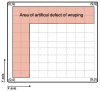
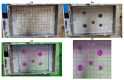
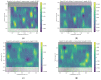
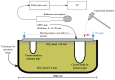
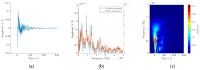
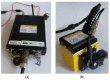
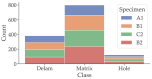
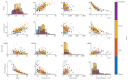
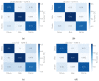
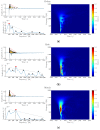
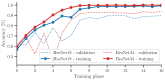
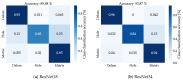
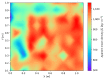
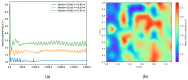
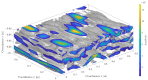
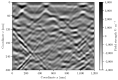
Sewage and water networks are crucial infrastructures of modern urban society. The uninterrupted functionality of these networks is paramount, necessitating regular maintenance and rehabilitation. In densely populated urban areas, trenchless methods, particularly those employing cured-in-place pipe technology, have emerged as the most cost-efficient approach for network rehabilitation. Common diagnostic methods for assessing pipe conditions, whether original or retrofitted with-cured-in-place pipes, typically include camera examination or laser scans, and are limited in material characterization. This study introduces three innovative methods for characterizing critical aspects of pipe conditions. The impact-echo method, ground-penetrating radar, and impedance spectroscopy address the challenges posed by polymer liners and offer enhanced accuracy in defect detection. These methods enable the characterization of delamination, identification of caverns behind cured-in-place pipes, and evaluation of overall pipe health. A machine learning algorithm using deep learning on images acquired from impact-echo signals using continuous wavelet transformation is presented to characterize defects. The aim is to compare traditional machine learning and deep learning methods to characterize selected pipe defects. The measurement conducted with ground-penetrating radar is depicted, employing a heuristic algorithm to estimate caverns behind the tested polymer composites. This study also presents results obtained through impedance spectroscopy, employed to characterize the delamination of polymer liners caused by uneven curing. A comparative analysis of these methods is conducted, assessing the accuracy by comparing the known positions of defects with their predicted characteristics based on laboratory measurements.
Keywords: cured-in-place pipes; machine learning; non-destructive testing; pipe defects; polymers; retrofitting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



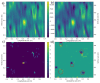
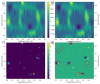
References
-
- Kaushal V., Najafi M., Serajiantehrani R., Malek Mohammadi M., Shirkhanloo S. Pipelines 2022. American Society of Civil Engineers; Reston, VA, USA: 2022. Construction Cost Comparison between Trenchless Cured-in-Place Pipe (CIPP) Renewal and Open-Cut Replacement for Sanitary Sewer Applications; pp. 171–177.
-
- Patil R.R., Ansari S.M., Calay R.K., Mustafa M.Y. Review of the State-of-the-art Sewer Monitoring and Maintenance Systems Pune Municipal Corporation—A Case Study. TEM J. 2021;10:1500–1508. doi: 10.18421/TEM104-02. - DOI
-
- Coombes P., Micevski T., Kuczera G. Deterioration, depreciation and serviceability of stormwater pipes; Proceedings of the Stormwater Industry Association 2002 Conference on Urban Stormwater Management; Orange, NSW, Australia. 23–24 April 2002.
-
- Trávníček P., Junga P., Kotek L., Vítěz T. Analysis of accidents at municipal wastewater treatment plants in Europe. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2022;74:104634. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2021.104634. - DOI
-
- Alam S., Sterling R.L., Allouche E., Condit W., Matthews J., Selvakumar A., Simicevic J. A retrospective evaluation of the performance of liner systems used to rehabilitate municipal gravity sewers. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015;50:451–464. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2015.08.011. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

