Which Is the Best Way to Treat Massive Hemoptysis? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies
- PMID: 38138876
- PMCID: PMC10744930
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13121649
Which Is the Best Way to Treat Massive Hemoptysis? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies
Abstract
Introduction: Hemoptysis is one of the most common symptoms of respiratory system diseases. Common causes include bronchiectasis, tumors, tuberculosis, aspergilloma, and cystic fibrosis. The severity of hemoptysis varies from mild to moderate to massive hemoptysis and can easily lead to hemodynamic instability and death from suffocation or shock. Nevertheless, the most threatening hemoptysis that is presented to the emergency department and requires hospitalization is the massive one. In these cases, today, the most common way to manage hemoptysis is bronchial artery embolization (BAE).
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed and Scopus from January 2017 (with the aim of selecting the newest possible reports in the literature) until May 2023 for studies reporting massive hemoptysis. All studies that included technical and clinical success rates of hemoptysis management, as well as rebleeding and mortality rates, were included. A proportional meta-analysis was conducted using a random-effects model.
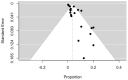
Results: Of the 30 studies included in this systematic review, 26 used bronchial artery embolization as a means of treating hemoptysis, with very high levels of both technical and clinical success (greater than 73.7% and 84.2%, respectively). However, in cases where it was not possible to use bronchial artery embolization, alternative methods were used, such as dual-vessel intervention (80% technical success rate and 66.7% clinical success rate), customized endobronchial silicone blockers (92.3% technical success rate and 92.3% clinical success rate), antifibrinolytic agents (50% clinical success rate), and percutaneous transthoracic embolization (93.1% technical success rate and 88.9% clinical success rate), which all had high success rates apart from antifibrinolytic agents. Of the 2467 patients included in these studies, 341 experienced rebleeding during the follow-up period, while 354 other complications occurred, including chest discomfort, fever, dysphagia, and paresis. A total of 89 patients died after an episode of massive hemoptysis or during the follow-up period. The results of the meta-analysis showed a pooled technical success of bronchial artery embolization equal to 97.22% and a pooled clinical success equal to 92.46%. The pooled recurrence was calculated to be 21.46%, while the mortality was 3.5%. These results confirm the ability of bronchial artery embolization in the treatment of massive hemoptysis but also emphasize the high rate of recurrence following the intervention, as well as the risk of death.
Conclusion: In conclusion, massive hemoptysis can be treated with great clinical and technical success using bronchial artery embolization, reducing mortality. Mortality has now been reduced to a small percentage of cases.
Keywords: bronchial artery embolization; management; massive hemoptysis; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
The efficacy, safety, and related factors of bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis with subgroup analysis.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024 Oct 31;14(5):859-877. doi: 10.21037/cdt-24-157. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024. PMID: 39513143 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchial Artery Embolization with Large Sized (700-900 µm) Tris-acryl Microspheres (Embosphere) for Massive Hemoptysis: Long-Term Results (Clinical Research).Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018 Feb;41(2):225-230. doi: 10.1007/s00270-017-1818-7. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29067512
-
The efficacy and safety of combined therapy with endobronchial tamponade and bronchial artery embolization for massive hemoptysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jul 3;24(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03116-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38961405 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchial artery embolization versus conservative treatment for hemoptysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Aug 30;24(1):428. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03244-x. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39215233 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis: a comprehensive review.Radiographics. 2002 Nov-Dec;22(6):1395-409. doi: 10.1148/rg.226015180. Radiographics. 2002. PMID: 12432111 Review.
Cited by
-
Palliative care in lung cancer: tumour- and treatment-related complications in lung cancer and their management.Breathe (Sheff). 2024 Nov 12;20(3):230203. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0203-2023. eCollection 2024 Oct. Breathe (Sheff). 2024. PMID: 39534495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 65-Year-Old Man with Refractory Hemoptysis Associated with Chronic Progressive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Who Failed to Respond to Combined Endobronchial Occlusion and Bronchial Artery Embolization: A Case Report and Literature Review.Am J Case Rep. 2024 Mar 13;25:e942422. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.942422. Am J Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38527273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Videothoracoscopic management of hemoptysis due to anomalous bronchial vessel treated with multiple bronchial artery embolizations: a case report.Front Pediatr. 2024 Nov 19;12:1431590. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1431590. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39629103 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Treatment of Obstructive Pneumonia with Hemoptysis due to Non-Absorbable Suture-Related Granulation.Surg Case Rep. 2025;11(1):25-0236. doi: 10.70352/scrj.cr.25-0236. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Surg Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40625541 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical profiles and mortality risk factors in pediatric pulmonary hemorrhage: a singlecenter study in Saudi Arabia.Ann Saudi Med. 2025 Jul-Aug;45(4):235-242. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2025.235. Epub 2025 Aug 7. Ann Saudi Med. 2025. PMID: 40753460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dudha M., Lehrman S., Aronow W.S., Rosa J. Hemoptysis: Diagnosis and treatment. Compr. Ther. 2009;35:139–149. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

