Is Wheat Glutenin Extract Intrinsically Allergenic? Evaluation Using a Novel Adjuvant-Free Mouse Model of Systemic Anaphylaxis
- PMID: 38139075
- PMCID: PMC10743909
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242417247
Is Wheat Glutenin Extract Intrinsically Allergenic? Evaluation Using a Novel Adjuvant-Free Mouse Model of Systemic Anaphylaxis
Abstract
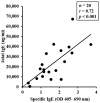
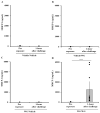
Wheat is a prominent allergenic food that can trigger life-threatening anaphylaxis. Presently, it remains unclear whether wheat glutenin (WG) extract possesses inherent sensitization potential independently, without the use of adjuvants, and whether it can sensitize mice to the extent of inducing life-threatening systemic anaphylaxis. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that repeated skin exposures to WG extract without adjuvant will sensitize mice with the resultant anaphylactic reaction upon systemic WG challenge. Balb/c mice were bred and maintained on a strict plant protein-free diet and were repeatedly exposed to a WG extract or vehicle once a week for 9 weeks. WG-specific (s)IgE and total (t)IgE levels were quantified. Mice were challenged with WG extract to induce anaphylactic reactions as measured by hypothermic shock response (HSR) and mucosal mast cell degranulation response (MMCR). We also conducted proteomic analysis of 120 spleen immune markers. These skin-sensitized mice exhibited exposure-dependent IgE responses and near-fatal anaphylaxis upon challenge. Proteomic analysis identified seven dramatically elevated immune biomarkers in anaphylactic mice. These data reveal that WG is intrinsically allergenic, and that chronic skin exposure to WG extract can prime the mice for potentially fatal anaphylaxis.
Keywords: IgE; glutenin allergy; mouse model; skin sensitization; systemic anaphylaxis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Venter C., Pereira B., Grundy J., Clayton C.B., Arshad S.H., Dean T. Prevalence of Sensitization Reported and Objectively Assessed Food Hypersensitivity amongst Six-Year-Old Children: A Population-Based Study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2006;17:356–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2006.00428.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)/National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA); Hatch project MICL02486 (Accession Number: 1012322), MICL02796, Hatch project MICL01699; Agricultural and Food Research Initiative Competitive Program, g/United States Department of Agriculture
- NIFA: MICL05103/United States Department of Agriculture
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

