Current Status and Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to Immunotherapy in Oral Malignant Melanoma
- PMID: 38139110
- PMCID: PMC10743423
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242417282
Current Status and Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to Immunotherapy in Oral Malignant Melanoma
Abstract
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), including anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) and anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1) antibodies, have initiated a new era in the treatment of malignant melanoma. ICIs can be used in various settings, including first-line, adjuvant, and neo-adjuvant therapy. In the scope of this review, we examined clinical studies utilizing ICIs in the context of treating oral mucosal melanoma, a rare disease, albeit with an extremely poor prognosis, with a specific focus on unraveling the intricate web of resistance mechanisms. The absence of a comprehensive review focusing on ICIs in oral mucosal melanoma is notable. Therefore, this review seeks to address this deficiency by offering a novel and thorough analysis of the current status, potential resistance mechanisms, and future prospects of applying ICIs specifically to oral malignant melanoma. Clarifying and thoroughly understanding these mechanisms will facilitate the advancement of effective therapeutic approaches and enhance the prospects for patients suffering from oral mucosal melanoma.
Keywords: anti-CTLA-4; anti-PD-1; immune checkpoint blockade; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immunotherapy; melanoma; oral mucosal melanoma; resistance mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
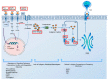
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immune Checkpoint Therapies for Melanoma.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2021 Feb;35(1):99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2020.08.013. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 33759776 Review.
-
Side effect management during immune checkpoint blockade using CTLA-4 and PD-1 antibodies for metastatic melanoma - an update.J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020 Jun;18(6):582-609. doi: 10.1111/ddg.14128. Epub 2020 Jun 3. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020. PMID: 32489011
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-angiogenic Agents in Combination With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Strategy for Cancer Treatment.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 25;11:1956. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01956. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immunotherapy for the treatment of melanoma, version 3.0.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Oct;11(10):e006947. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-006947. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37852736 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting metabolic reprogramming to overcome immune tolerance in melanoma immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1597770. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1597770. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hallmarks of cancer resistance.iScience. 2024 May 15;27(6):109979. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109979. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38832007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo study on IL-37 inhibition of malignant melanoma metastasis.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Dec 28;49(12):1885-1890. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.230570. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 40195660 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Advances in Melanoma and Skin Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 21;26(5):1849. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051849. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zito P.M., Brizuela M., Mazzoni T. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2023. Oral Melanoma. - PubMed
-
- Samudio-Scavone E.M. Pigmented Melanoma of the Tongue. Instituto de Previsión Social. Case Report. Cirugía Paraguaya. 2023;47:33–35. doi: 10.18004/sopaci.2023.abril.33. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

