Development of Single-Segment Substitution Lines and Fine-Mapping of qSPP4 for Spikelets Per Panicle and qGW9 for Grain Width Based on Rice Dual-Segment Substitution Line Z783
- PMID: 38139135
- PMCID: PMC10744095
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242417305
Development of Single-Segment Substitution Lines and Fine-Mapping of qSPP4 for Spikelets Per Panicle and qGW9 for Grain Width Based on Rice Dual-Segment Substitution Line Z783
Abstract
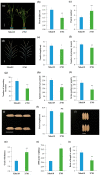
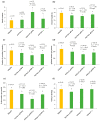
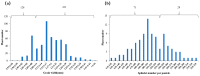
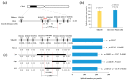
Single segment substitution line (SSSL) libraries are an ideal platform for breeding by design. To develop SSSLs-Xihui18 covering the whole genome, a novel rice chromosome segment substitution line (CSSL), Z783, carrying two substitution segments (average length of 6.55 Mb) on Chr.4 and Chr.9 was identified, which was a gap in the library previously. Z783 was developed from the progeny of recipient "Xihui18" (an indica restorer line) and donor "Huhan3" (a japonica cultivar) by advanced backcross combined molecular marker-assisted selection (MAS). It displayed multiple panicles and less spikelets and wide grains. Then, a F2 population derived from Xihui18/Z783 was used to map quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for yield-related traits by the mixed linear model method. Nine QTLs were detected (p < 0.05). Furthermore, three SSSLs were constructed by MAS, and all 9 QTLs could be validated, and 15 novel QTLs could be detected by these SSSLs by a one-way ANOVA analysis. The genetic analysis showed that qSSP4 for less spikelets and qGW9 for wide grain all displayed dominant gene action in their SSSLs. Finally, qSSP4 and qGW9 were fine-mapped to intervals of 2.75 Mb and 1.84 Mb, on Chromosomes 4 and 9, respectively. The results lay a solid foundation for their map cloning and molecular breeding by design.
Keywords: QTL; additive effect; chromosomal segment substitution line; grain number and size.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genetic dissection of QTL for important agronomic traits and fine-mapping of qGL4 and qGW6 based on a short-width grain rice CSSL-Z691.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Mar 10;16:1539625. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1539625. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40129748 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Effects Analysis of QTLs for Rice Grain Size Based on CSSL-Z403 and Its Dissected Single and Dual-Segment Substitution Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 27;24(15):12013. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512013. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569388 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, pyramid, and candidate gene of QTL for yield-related traits based on rice CSSLs in indica Xihui18 background.Mol Breed. 2022 Mar 24;42(4):19. doi: 10.1007/s11032-022-01284-x. eCollection 2022 Apr. Mol Breed. 2022. PMID: 37309460 Free PMC article.
-
2Gs and plant architecture: breaking grain yield ceiling through breeding approaches for next wave of revolution in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024 Feb;44(1):139-162. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2022.2112648. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 36176065 Review.
-
Marker-assisted selection for grain number and yield-related traits of rice (Oryza sativa L.).Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2020 May;26(5):885-898. doi: 10.1007/s12298-020-00773-7. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2020. PMID: 32377039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic dissection of QTL for important agronomic traits and fine-mapping of qGL4 and qGW6 based on a short-width grain rice CSSL-Z691.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Mar 10;16:1539625. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1539625. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40129748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruinsma J. The Resource Outlook to 2050: By How Much Do Land, Water and Crop Yields Need to Increase by 2050? Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO); Rome, Italy: 2009.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

