Shake It Up Baby Now: The Changing Focus on TWIST1 and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer and Other Diseases
- PMID: 38139368
- PMCID: PMC10743446
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242417539
Shake It Up Baby Now: The Changing Focus on TWIST1 and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer and Other Diseases
Abstract
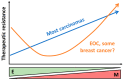
TWIST1 is a transcription factor that is necessary for healthy neural crest migration, mesoderm development, and gastrulation. It functions as a key regulator of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process by which cells lose their polarity and gain the ability to migrate. EMT is often reactivated in cancers, where it is strongly associated with tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Early work on TWIST1 in adult tissues focused on its transcriptional targets and how EMT gave rise to metastatic cells. In recent years, the roles of TWIST1 and other EMT factors in cancer have expanded greatly as our understanding of tumor progression has advanced. TWIST1 and related factors are frequently tied to cancer cell stemness and changes in therapeutic responses and thus are now being viewed as attractive therapeutic targets. In this review, we highlight non-metastatic roles for TWIST1 and related EMT factors in cancer and other disorders, discuss recent findings in the areas of therapeutic resistance and stemness in cancer, and comment on the potential to target EMT for therapy. Further research into EMT will inform novel treatment combinations and strategies for advanced cancers and other diseases.
Keywords: TWIST1; cancer stem cells; drug resistance; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; novel therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The interplay between microRNAs and Twist1 transcription factor: a systematic review.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7007-19. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4960-y. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26880587
-
USP6NL knockdown suppresses colorectal cancer progression by inducing CASP9-Mediated apoptosis and disrupting FOXC2/SNAI1-Driven EMT and angiogenesis.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jul 11;25(1):153. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01663-5. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40643716
-
TGF-β1 exposure induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition both in CSCs and non-CSCs of the A549 cell line, leading to an increase of migration ability in the CD133+ A549 cell fraction.Cell Death Dis. 2013 May 2;4(5):e620. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.144. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23640462 Free PMC article.
-
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 increases invasion of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-associated cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by modifying transforming growth factor-β signalling.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Dec 23;192(1):104-117. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae295. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39018437 Free PMC article.
-
What is the Impact of Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Solid Tumours: A Qualitative Systematic Review and Quantitative Meta-Analysis.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Feb 24;21(5):2155-2178. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.107045. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40083695 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The chromatin landscape of high-grade serous ovarian cancer metastasis identifies regulatory drivers in post-chemotherapy residual tumour cells.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 28;7(1):1211. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06909-9. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39341888 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miRNA‑214‑3p in cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2025 Oct;54(4):123. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8957. Epub 2025 Aug 1. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40747717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TNFSF14-HVEM/LTβR Exacerbates Keratinocyte Abnormalities and IMQ-Induced Psoriatic Skin Inflammation via Activating NF-κB/TWIST1 Signalling Pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Aug;29(15):e70774. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70774. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40768619 Free PMC article.
-
Putative Biomarkers for Prognosis, Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition, and Drug Response in Cell Lines Representing Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression.Genes (Basel). 2025 Feb 9;16(2):209. doi: 10.3390/genes16020209. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40004538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sasaki A., Abe H., Mochizuki S., Shimoda M., Okada Y. SOX4, an Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Inducer, Transactivates ADAM28 Gene Expression and Co-localizes with ADAM28 at the Invasive Front of Human Breast and Lung Carcinomas. Pathol. Int. 2018;68:449–458. doi: 10.1111/pin.12685. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Platt J.B. Ontogenetische Differenzirung Des Ektoderms in Necturus. Arch. für Mikrosk. Anat. 1894;43:911–966. doi: 10.1007/BF02933885. - DOI
-
- Chang A.T., Liu Y., Ayyanathan K., Benner C., Jiang Y., Prokop J.W., Paz H., Wang D., Li H.R., Fu X.D., et al. An Evolutionarily Conserved DNA Architecture Determines Target Specificity of the TWIST Family BHLH Transcription Factors. Genes. Dev. 2015;29:603–616. doi: 10.1101/gad.242842.114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

