Toward Sensor Measurement Reliability in Blockchains
- PMID: 38139505
- PMCID: PMC10747797
- DOI: 10.3390/s23249659
Toward Sensor Measurement Reliability in Blockchains
Abstract
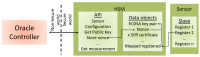
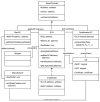
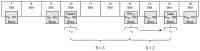
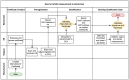
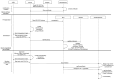
In this work, a secure architecture to send data from an Internet of Things (IoT) device to a blockchain-based supply chain is presented. As is well known, blockchains can process critical information with high security, but the authenticity and accuracy of the stored and processed information depend primarily on the reliability of the information sources. When this information requires acquisition from uncontrolled environments, as is the normal situation in the real world, it may be, intentionally or unintentionally, erroneous. The entities that provide this external information, called Oracles, are critical to guarantee the quality and veracity of the information generated by them, thus affecting the subsequent blockchain-based applications. In the case of IoT devices, there are no effective single solutions in the literature for achieving a secure implementation of an Oracle that is capable of sending data generated by a sensor to a blockchain. In order to fill this gap, in this paper, we present a holistic solution that enables blockchains to verify a set of security requirements in order to accept information from an IoT Oracle. The proposed solution uses Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) to address the security requirements of integrity and device trustworthiness, as well as a novel Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) based on a blockchain for authenticity, traceability, and data freshness. The solution is then implemented on Ethereum and evaluated regarding the fulfillment of the security requirements and time response. The final design has some flexibility limitations that will be approached in future work.
Keywords: Internet of Things (IoT); blockchain; hardware oracle; public key infrastructure (PKI); smart contract; trustworthiness.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Ernesto Gómez-Marín was employed by the company Infineon Technologies AG. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abdirad M., Krishnan K. Industry 4.0 in Logistics and Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Eng. Manag. J. 2021;33:187–201. doi: 10.1080/10429247.2020.1783935. - DOI
-
- Talwar S., Kaur P., Fosso Wamba S., Dhir A. Big Data in operations and supply chain management: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021;59:3509–3534. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2020.1868599. - DOI
-
- Kumar D., Singh R.K., Mishra R., Daim T.U. Roadmap for integrating blockchain with Internet of Things (IoT) for sustainable and secured operations in logistics and supply chains: Decision making framework with case illustration. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023;196:122837. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122837. - DOI
-
- Varriale V., Cammarano A., Michelino F., Caputo M. Integrating blockchain, RFID and IoT within a cheese supply chain: A cost analysis. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2023;34:100486. doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2023.100486. - DOI
-
- Kumar M., Choubey V.K., Raut R.D., Jagtap S. Enablers to achieve zero hunger through IoT and blockchain technology and transform the green food supply chain systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2023;405:136894. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136894. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

