Integrated Controller Design and Application for CNC Machine Tool Servo Systems Based on Model Reference Adaptive Control and Adaptive Sliding Mode Control
- PMID: 38139600
- PMCID: PMC10747934
- DOI: 10.3390/s23249755
Integrated Controller Design and Application for CNC Machine Tool Servo Systems Based on Model Reference Adaptive Control and Adaptive Sliding Mode Control
Abstract
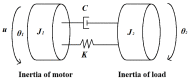
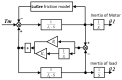
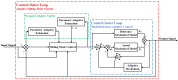
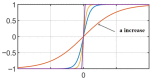
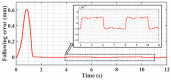
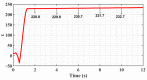
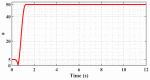
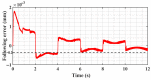
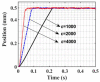
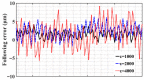
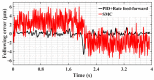
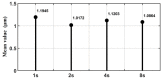
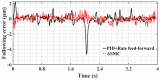
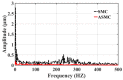
In order to reduce the effect of nonlinear friction and time-varying factors on the servo system of a computer numerical control (CNC) machine tool and improve its motion control accuracy, this paper uses an adaptive sliding mode control (ASMC) method based on model reference adaptive control (MRAC). The method adopts ASMC in the control outer loop and obtains the optimal control parameters by making the sliding mode control (SMC) law continuous and adaptively estimating the control parameters. At the same time, MRAC is used in the control inner loop to enhance the "invariance" of the controlled object so that the switching gain of SMC can satisfy the disturbance matching condition even under lesser conditions. Simulation and experimental results show that compared with the traditional SMC, the ASMC based on MRAC proposed in this paper effectively reduces the influence of nonlinear friction on the system performance, and the reduction in following error reaches 71.2%, which significantly improves the motion control accuracy of the control system. The spectral analysis of the following errors shows that the maximum magnitude reduction rate of the high-frequency chattering is 89.02%, which significantly reduces the effect of the high-frequency chattering and effectively improves the stability performance of the control system.
Keywords: adaptive sliding mode control; dynamics model for CNC machines; model reference adaptive control; nonlinear friction.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Gai, H. was employed by the company Qilu Division, Sinopec Catalyst Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Adaptive fuzzy PID cross coupled control for multi-axis motion system based on sliding mode disturbance observation.Sci Prog. 2021 Apr-Jun;104(2):368504211011847. doi: 10.1177/00368504211011847. Sci Prog. 2021. PMID: 33913385 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of motion accuracy and energy consumption for industrial feed drive systems using adaptive sliding mode control.ISA Trans. 2020 Nov;106:382-391. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.06.025. Epub 2020 Jul 21. ISA Trans. 2020. PMID: 32896386
-
A new adaptive sliding mode controller based on the RBF neural network for an electro-hydraulic servo system.ISA Trans. 2022 Oct;129(Pt A):472-484. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2021.12.044. Epub 2022 Jan 10. ISA Trans. 2022. PMID: 35067353
-
Incomplete differentiation-based improved adaptive backstepping integral sliding mode control for position control of hydraulic system.ISA Trans. 2021 Mar;109:199-217. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.10.027. Epub 2020 Oct 6. ISA Trans. 2021. PMID: 33059903
-
Optimal third-order sliding mode controller for dual star induction motor based on grey wolf optimization algorithm.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 7;10(12):e32669. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32669. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39183859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multivariable Iterative Learning Control Design for Precision Control of Flexible Feed Drives.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 30;24(11):3536. doi: 10.3390/s24113536. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38894327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Åström K.J., Hägglund T. The future of PID control. Control Eng. Pract. 2001;9:1163–1175. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(01)00062-4. - DOI
-
- Yesmin A., Bera M.K. Design of event-triggered sliding mode controller based on reaching law with time varying event generation approach. Eur. J. Control. 2019;48:30–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcon.2018.12.003. - DOI
-
- Chen Y., Wei Y., Zhong H., Wang Y. Sliding mode control with a second-order switching law for a class of nonlinear fractional order systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016;85:633–643. doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-2712-6. - DOI
-
- Chen Y., Li A., Li H., Yang X., Chen W. Sensorless Control Method for SPMSMs Based on Improved Sliding Mode Reaching Rate. Electronics. 2023;12:3720. doi: 10.3390/electronics12173720. - DOI
-
- Taleb M., Plestan F., Bououlid B. Higher order sliding mode control based on adaptive first order sliding mode controller. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014;47:1380–1385. doi: 10.3182/20140824-6-ZA-1003.02487. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

