The Acceptance of Cream Soups with the Addition of Edible Insects (Mealworm, T. molitor; House Cricket, A. domesticus; Buffalo Worm, A. diaperinus; Grasshopper, R. differens) among Young People and Seniors in Poland
- PMID: 38140306
- PMCID: PMC10745299
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15245047
The Acceptance of Cream Soups with the Addition of Edible Insects (Mealworm, T. molitor; House Cricket, A. domesticus; Buffalo Worm, A. diaperinus; Grasshopper, R. differens) among Young People and Seniors in Poland
Abstract
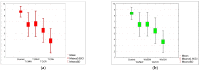
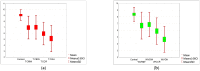
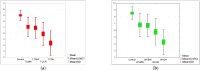
Research on the acceptance of consuming insects in one's diet shows the increasing importance of this issue in the context of a sustainable food chain and ecology. Insects represent a promising food source due to their high nutritional value, efficiency in production, and minimal environmental impact, as well as the growing awareness of ecological issues. Despite these benefits, cultural and psychological barriers hinder the acceptance of consuming insects in Western countries. In this study, an assessment was made of the acceptance level of cream-type soups made from tomatoes and white vegetables with the addition of 20% flour from four insect species: mealworm (T. molitor); house cricket (A. domesticus); buffalo worm (A. diaperinus); and grasshopper (R. differens), compared to a control sample. One hundred and four subjects (55 seniors and 49 young adults) participated in this study. The acceptance level of various soups with insect flour was evaluated, considering different sensory parameters such as appearance, smell, taste, and texture. The research showed that older people have a lower acceptance for dishes containing insects compared to young adults, but the differences in the responses given were not statistically significant (p = 0.05), rejecting the assumption that insect-based products should be mainly targeted at young people. Of all the proposed test samples, the mealworm (T. molitor) was the most acceptable insect species in the tests in both taste versions for both age groups. The average score was 6.63 points on a 10-point scale. The products with the addition of grasshopper (R. differens) were rated the lowest. The acceptance level ranged between 4.23 and 4.38 points. A multiple regression analysis showed that taste and texture had the strongest influence on the overall acceptance of these dishes, and the results obtained were highly correlated with the general opinion of the testers. The increasing acceptance level and growing interest in this type of food can be a positive step towards sustainable and efficient food production.
Keywords: buffalo worm; consumer acceptance; edible insects; grasshopper; house cricket; mealworm; soup.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acceptance of Muffins (Sweet and Savory) with the Addition of T. molitor, A. diaperinus, A. domesticus, R. differens, Considering Psychological Factors (Food Neophobia Scale, Consumer Attitude).Foods. 2024 Jun 1;13(11):1735. doi: 10.3390/foods13111735. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38890963 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Composition of Nut Bars with Addition of Various Edible Insect Flours.Molecules. 2023 Apr 18;28(8):3556. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083556. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110790 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition, Nutritional Value, and Acceptance of Nut Bars with the Addition of Edible Insect Powder.Molecules. 2022 Dec 2;27(23):8472. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238472. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500560 Free PMC article.
-
Proteins and Amino Acids from Edible Insects for the Human Diet-A Narrative Review Considering Environmental Sustainability and Regulatory Challenges.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 2;17(7):1245. doi: 10.3390/nu17071245. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40219002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An analysis of emerging food safety and fraud risks of novel insect proteins within complex supply chains.NPJ Sci Food. 2024 Jan 20;8(1):7. doi: 10.1038/s41538-023-00241-y. NPJ Sci Food. 2024. PMID: 38245539 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Willingness to Consume and Purchase Food with Edible Insects among Generation Z in Poland.Foods. 2024 Jul 12;13(14):2202. doi: 10.3390/foods13142202. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39063286 Free PMC article.
-
Acceptance of Muffins (Sweet and Savory) with the Addition of T. molitor, A. diaperinus, A. domesticus, R. differens, Considering Psychological Factors (Food Neophobia Scale, Consumer Attitude).Foods. 2024 Jun 1;13(11):1735. doi: 10.3390/foods13111735. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38890963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- del Hierro J.N., Hernández-Ledesma B., Martin D. Current Advances for Development of Functional Foods Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2022. Potential of edible insects as a new source of bioactive compounds against metabolic syndrome; pp. 331–364.
-
- Boukid F., Sogari G., Rosell C.M. Edible insects as foods: Mapping scientific publications and product launches in the global market (1996–2021) J. Insects Food Feed. 2023;9:353–368. doi: 10.3920/JIFF2022.0060. - DOI
-
- Meshulam-Pascoviche D., David-Birman T., Refael G., Lesmes U. Big opportunities for tiny bugs: Processing effects on the techno-functionality and digestibility of edible insects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022;122:265–274. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.02.012. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

