Advances in Research on Marine-Derived Lipid-Lowering Active Substances and Their Molecular Mechanisms
- PMID: 38140377
- PMCID: PMC10745522
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15245118
Advances in Research on Marine-Derived Lipid-Lowering Active Substances and Their Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
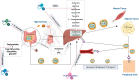
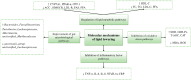
Hyperlipidemia (HLP) is a metabolic disorder caused by abnormal lipid metabolism. Recently, the prevalence of HLP caused by poor dietary habits in the population has been increasing year by year. In addition, lipid-lowering drugs currently in clinical use have shown significant improvement in blood lipid levels, but are accompanied by certain side effects. However, bioactive marine substances have been shown to possess a variety of physiological activities such as hypoglycemic, antioxidant, antithrombotic and effects on blood pressure. Therefore, the hypolipidemic efficacy of marine bioactive substances with complex and diverse structures has also attracted attention. This paper focuses on the therapeutic role of marine-derived polysaccharides, unsaturated fatty acids, and bioactive peptides in HLP, and briefly discusses the main mechanisms by which these substances exert their hypolipidemic activity in vivo.
Keywords: hyperlipidemia; lipid metabolism; marine bioactive substances; molecular mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Research advances on hypolipidemic effect of polysaccharides].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Sep;43(17):3451-3459. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20180419.008. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30347911 Review. Chinese.
-
An Insight into Antihyperlipidemic Effects of Polysaccharides from Natural Resources.Molecules. 2022 Mar 15;27(6):1903. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061903. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of quercetin and its glycosides].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Dec;40(23):4560-7. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 27141664 Review. Chinese.
-
Advances in the Study of Marine Products with Lipid-Lowering Properties.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jul 27;18(8):390. doi: 10.3390/md18080390. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32726987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypolipidemic Components from Medicine Food Homology Species Used in China: Pharmacological and Health Effects.Arch Med Res. 2017 Oct;48(7):569-581. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Arch Med Res. 2017. PMID: 29452699 Review.
Cited by
-
Peptides from Harpadon nehereus Bone Ameliorate Sodium Palmitate-Induced HepG2 Lipotoxicity by Regulating Oxidative Stress and Lipid Metabolism.Mar Drugs. 2025 Mar 9;23(3):118. doi: 10.3390/md23030118. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40137304 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Peptides Derived from Tuna: Screening, Extraction, Bioactivity, and Mechanism of Action.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jul 21;23(7):293. doi: 10.3390/md23070293. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Clinical Impact of a Polyphenol-Rich Extract from Salicornia ramosissima on Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack and Minor Stroke.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 13;16(24):4307. doi: 10.3390/nu16244307. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39770931 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Virtual screening and evaluation of bioactive peptides from Haliotis discus hannai as potential HMGCR inhibitors for hyperlipidemia treatment.Front Nutr. 2024 Dec 30;11:1525768. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1525768. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39811675 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Hydrolysis of Earthworm Protein and the Lipid-Lowering Mechanism of Peptides in the Hydrolysate.Foods. 2025 Jul 1;14(13):2338. doi: 10.3390/foods14132338. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40647090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee N., Tom B., Dawit Z. Global Trends in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Ther. 2023;45:1087–1091. - PubMed
-
- Hung P.M., Thanh V.H., Van Sy H., Duc D.Q., Tuan V.A., Tran A.T., Brizuela G.E., Tran H.B. Adherence to hypertension and dyslipidemia treatment and its implication on control of cardiovascular disease in Vietnam: A semi-systematic review. Medicine. 2022;101:e32137. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032137. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

